The transcription factor lymphoid enhancer factor 1 controls invariant natural killer T cell expansion and Th2-type effector differentiation
- PMID: 25897173
- PMCID: PMC4419352
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20141849
The transcription factor lymphoid enhancer factor 1 controls invariant natural killer T cell expansion and Th2-type effector differentiation
Abstract
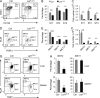
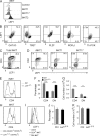
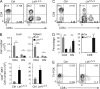
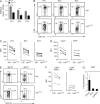
Invariant natural killer T cells (iNKT cells) are innate-like T cells that rapidly produce cytokines that impact antimicrobial immune responses, asthma, and autoimmunity. These cells acquire multiple effector fates during their thymic development that parallel those of CD4(+) T helper cells. The number of Th2-type effector iNKT cells is variable in different strains of mice, and their number impacts CD8 T, dendritic, and B cell function. Here we demonstrate a unique function for the transcription factor lymphoid enhancer factor 1 (LEF1) in the postselection expansion of iNKT cells through a direct induction of the CD127 component of the receptor for interleukin-7 (IL-7) and the transcription factor c-myc. LEF1 also directly augments expression of the effector fate-specifying transcription factor GATA3, thus promoting the development of Th2-like effector iNKT cells that produce IL-4, including those that also produce interferon-γ. Our data reveal LEF1 as a central regulator of iNKT cell number and Th2-type effector differentiation.
© 2015 Carr et al.
Figures




References
-
- Bedel R., Berry R., Mallevaey T., Matsuda J.L., Zhang J., Godfrey D.I., Rossjohn J., Kappler J.W., Marrack P., and Gapin L.. 2014. Effective functional maturation of invariant natural killer T cells is constrained by negative selection and T-cell antigen receptor affinity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 111:E119–E128 10.1073/pnas.1320777110 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

