Quinoline-based clioquinol and nitroxoline exhibit anticancer activity inducing FoxM1 inhibition in cholangiocarcinoma cells
- PMID: 25897210
- PMCID: PMC4396583
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S79313
Quinoline-based clioquinol and nitroxoline exhibit anticancer activity inducing FoxM1 inhibition in cholangiocarcinoma cells
Abstract
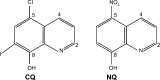
Purpose: Fork head box M1 (FoxM1) is an oncogenic transcription factor frequently elevated in numerous cancers, including cholangiocarcinoma (CCA). A growing body of evidence documents its diverse functions contributing to tumorigenesis and cancer progression. As such, discovery of agents that can target FoxM1 would be valuable for the treatment of CCA. The quinoline-based compounds, namely clioquinol (CQ) and nitroxoline (NQ), represent a new class of anticancer drug. However, their efficacy and underlying mechanisms have not been elucidated in CCA. In this study, anticancer activities and inhibitory effects of CQ and NQ on FoxM1 signaling were explored using CCA cells.
Methods: The effects of CQ and NQ on cell viability and proliferation were evaluated using the colorimetric 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium (MTS assay). Colony formation and cell migration affected by CQ and NQ were investigated using a clonogenic and a wound healing assay, respectively. To demonstrate the agents' effects on FoxM1 signaling, expression levels of the target genes were quantitatively determined using real-time polymerase chain reaction.
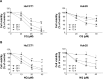
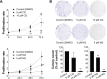
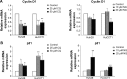
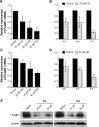
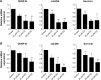
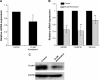
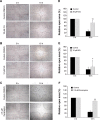
Results: CQ and NQ significantly inhibited cell survival of HuCCT1 and Huh28 in a dose- and a time-dependent fashion. Further investigations using the rapidly proliferating HuCCT1 cells revealed significant suppression of cell proliferation and colony formation induced by low doses of the compounds. Treatment of CQ and NQ repressed expression of cyclin D1 but enhanced expression of p21. Most importantly, upon CQ and NQ treatment, expression of oncogenic FoxM1 was markedly decreased concomitant with downregulation of various FoxM1's downstream targets including cdc25b, CENP-B, and survivin. In addition, the compounds distinctly impaired HuCCT1 migration as well as inhibited expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9.
Conclusion: Collectively, this study reports for the first time the anticancer effects of CQ and NQ against CCA cells, and highlights new insights into the mechanism of actions of the quinoline-based compounds to disrupt FoxM1 signaling.
Keywords: 8-hydroxyquinoline derivatives; FoxM1; cholangiocarcinoma; clioquinol; migration; nitroxoline.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nitroxoline (8-hydroxy-5-nitroquinoline) is more a potent anti-cancer agent than clioquinol (5-chloro-7-iodo-8-quinoline).Cancer Lett. 2011 Dec 15;312(1):11-7. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2011.06.032. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Cancer Lett. 2011. PMID: 21899946 Free PMC article.
-
Allicin Inhibits Proliferation and Invasion in Vitro and in Vivo via SHP-1-Mediated STAT3 Signaling in Cholangiocarcinoma.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(2):641-653. doi: 10.1159/000490019. Epub 2018 May 22. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29794468
-
Curcumin-mediated regulation of Notch1/hairy and enhancer of split-1/survivin: molecular targeting in cholangiocarcinoma.J Surg Res. 2015 Oct;198(2):434-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2015.03.029. Epub 2015 Mar 19. J Surg Res. 2015. PMID: 25890434 Review.
-
Co-targeting of Cyclooxygenase-2 and FoxM1 is a viable strategy in inducing anticancer effects in colorectal cancer cells.Mol Cancer. 2015 Jul 10;14:131. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0406-1. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26159723 Free PMC article.
-
FOXM1 (Forkhead box M1) in tumorigenesis: overexpression in human cancer, implication in tumorigenesis, oncogenic functions, tumor-suppressive properties, and target of anticancer therapy.Adv Cancer Res. 2013;119:191-419. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407190-2.00016-2. Adv Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23870513 Review.
Cited by
-
Nitroxoline inhibits bladder cancer progression by reversing EMT process and enhancing anti-tumor immunity.J Cancer. 2020 Sep 23;11(22):6633-6641. doi: 10.7150/jca.47025. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33046984 Free PMC article.
-
Derivatives (halogen, nitro and amino) of 8-hydroxyquinoline with highly potent antimicrobial and antioxidant activities.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2016 Mar 24;6:135-141. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2016.03.014. eCollection 2016 Jul. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2016. PMID: 29214226 Free PMC article.
-
Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of N-Picolineamides as Trypanosoma cruzi Antiproliferative Agents.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2023 Jan 3;14(1):59-65. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.2c00425. eCollection 2023 Jan 12. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2023. PMID: 36655123 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the mechanism of antifungal action of 8-hydroxyquinolines.Saudi Pharm J. 2019 Jan;27(1):41-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2018.07.017. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Saudi Pharm J. 2019. PMID: 30662305 Free PMC article.
-
Organoruthenated Nitroxoline Derivatives Impair Tumor Cell Invasion through Inhibition of Cathepsin B Activity.Inorg Chem. 2019 Sep 16;58(18):12334-12347. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b01882. Epub 2019 Aug 29. Inorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 31464130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matull WR, Khan SA, Pereira SP. Re: impact of classification of hilar cholangiocarcinomas (Klatskin tumors) on incidence of intra- and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99(5):407. author reply 407–408. - PubMed
-
- Thongprasert S, Napapan S, Charoentum C, Moonprakan S. Phase II study of gemcitabine and cisplatin as first-line chemotherapy in inoperable biliary tract carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 2005;16(2):279–281. - PubMed
-
- Lee GW, Kang JH, Kim HG, Lee JS, Lee JS, Jang JS. Combination chemotherapy with gemcitabine and cisplatin as first-line treatment for immunohistochemically proven cholangiocarcinoma. Am J Clin Oncol. 2006;29(2):127–131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

