Colorimetric biosensing of targeted gene sequence using dual nanoparticle platforms
- PMID: 25897217
- PMCID: PMC4396418
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S74753
Colorimetric biosensing of targeted gene sequence using dual nanoparticle platforms
Abstract
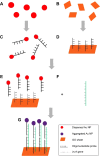
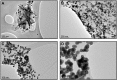
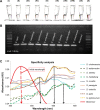
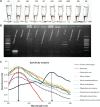
We have developed a colorimetric biosensor using a dual platform of gold nanoparticles and graphene oxide sheets for the detection of Salmonella enterica. The presence of the invA gene in S. enterica causes a change in color of the biosensor from its original pinkish-red to a light purplish solution. This occurs through the aggregation of the primary gold nanoparticles-conjugated DNA probe onto the surface of the secondary graphene oxide-conjugated DNA probe through DNA hybridization with the targeted DNA sequence. Spectrophotometry analysis showed a shift in wavelength from 525 nm to 600 nm with 1 μM of DNA target. Specificity testing revealed that the biosensor was able to detect various serovars of the S. enterica while no color change was observed with the other bacterial species. Sensitivity testing revealed the limit of detection was at 1 nM of DNA target. This proves the effectiveness of the biosensor in the detection of S. enterica through DNA hybridization.
Keywords: DNA hybridization; DNA probe; Salmonella enterica; biosensor; gold nanoparticles; graphene oxide.
Figures

References
-
- Sheng X, Zhang H, Xia Q, Xu S, Xu H, Huang X. Mig-14 plays an important role in influencing gene expression of Salmonella enterica serovar typhi, which contributes to cell invasion under hyperosmotic conditions. Res Microbiol. 2013;164(9):903–912. - PubMed
-
- Toboldt A, Tietze E, Helmuth R, Junker E, Fruth A, Malorny B. Molecular epidemiology of Salmonella enterica serovar Kottbus isolated in Germany from humans, food and animals. Vet Microbiol. 2014;170(1–2):97–108. - PubMed
-
- Lee C-J, Su L-H, Huang Y-C, Chiu C-H. First isolation of ciprofloxacin-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar typhi in Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2013;46(6):469–473. - PubMed
-
- Lee SJ, Gebru Awji E, Kim MH, Park SC. BaeR protein from Salmonella enterica serovar paratyphi A induces inflammatory response in murine and human cell lines. Microbes Infect. 2013;15(13):951–957. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

