Piccolo Directs Activity Dependent F-Actin Assembly from Presynaptic Active Zones via Daam1
- PMID: 25897839
- PMCID: PMC4405365
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120093
Piccolo Directs Activity Dependent F-Actin Assembly from Presynaptic Active Zones via Daam1
Abstract
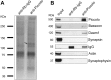
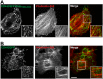
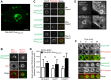
The dynamic assembly of filamentous (F) actin plays essential roles in the assembly of presynaptic boutons, the fusion, mobilization and recycling of synaptic vesicles (SVs), and presynaptic forms of plasticity. However, the molecular mechanisms that regulate the temporal and spatial assembly of presynaptic F-actin remain largely unknown. Similar to other F-actin rich membrane specializations, presynaptic boutons contain a set of molecules that respond to cellular cues and trans-synaptic signals to facilitate activity-dependent assembly of F-actin. The presynaptic active zone (AZ) protein Piccolo has recently been identified as a key regulator of neurotransmitter release during SV cycling. It does so by coordinating the activity-dependent assembly of F-Actin and the dynamics of key plasticity molecules including Synapsin1, Profilin and CaMKII. The multidomain structure of Piccolo, its exquisite association with the AZ, and its ability to interact with a number of actin-associated proteins suggest that Piccolo may function as a platform to coordinate the spatial assembly of F-actin. Here we have identified Daam1, a Formin that functions with Profilin to drive F-actin assembly, as a novel Piccolo binding partner. We also found that within cells Daam1 activation promotes Piccolo binding, an interaction that can spatially direct the polymerization of F-Actin. Moreover, similar to Piccolo and Profilin, Daam1 loss of function impairs presynaptic-F-actin assembly in neurons. These data suggest a model in which Piccolo directs the assembly of presynaptic F-Actin from the AZ by scaffolding key actin regulatory proteins including Daam1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Piccolo regulates the dynamic assembly of presynaptic F-actin.J Neurosci. 2011 Oct 5;31(40):14250-63. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1835-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21976510 Free PMC article.
-
Trio, a Rho Family GEF, Interacts with the Presynaptic Active Zone Proteins Piccolo and Bassoon.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 1;11(12):e0167535. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167535. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27907191 Free PMC article.
-
Unitary assembly of presynaptic active zones from Piccolo-Bassoon transport vesicles.Neuron. 2003 Apr 24;38(2):237-52. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00207-1. Neuron. 2003. PMID: 12718858
-
Role of Bassoon and Piccolo in Assembly and Molecular Organization of the Active Zone.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2016 Jan 12;7:19. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2015.00019. eCollection 2015. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26793095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular organization and assembly of the presynaptic active zone of neurotransmitter release.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2006;43:49-68. doi: 10.1007/400_012. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2006. PMID: 17068967 Review.
Cited by
-
The presynaptic scaffolding protein Piccolo organizes the readily releasable pool at the calyx of Held.J Physiol. 2018 Apr 15;596(8):1485-1499. doi: 10.1113/JP274885. Epub 2018 Jan 4. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29194628 Free PMC article.
-
Piccolo is essential for the maintenance of mouse retina but not cochlear hair cell function.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Apr 21;13(8):11678-11695. doi: 10.18632/aging.202861. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33882456 Free PMC article.
-
Daam1 regulates fascin for actin assembly in mouse oocyte meiosis.Cell Cycle. 2017 Jul 18;16(14):1350-1356. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1325045. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Cell Cycle. 2017. PMID: 28682694 Free PMC article.
-
Formin DAAM1 Organizes Actin Filaments in the Cytoplasmic Nodal Actin Network.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 19;11(10):e0163915. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163915. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27760153 Free PMC article.
-
The axonal cytoskeleton: from organization to function.Front Mol Neurosci. 2015 Aug 14;8:44. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2015.00044. eCollection 2015. Front Mol Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26321907 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sudhof TC. The synaptic vesicle cycle. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2004;27:509–47. . - PubMed
-
- Schoch S, Gundelfinger ED. Molecular organization of the presynaptic active zone. Cell Tissue Res. 2006;326(2):379–91. . - PubMed
-
- Rosenmund C, Rettig J, Brose N. Molecular mechanisms of active zone function. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003;13(5):509–19. . - PubMed
-
- Greengard P, Benfenati F, Valtorta F. Synapsin I, an actin-binding protein regulating synaptic vesicle traffic in the nerve terminal. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1994;29:31–45. Epub 1994/01/01. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

