Resveratrol Rescues the Impairments of Hippocampal Neurons Stimulated by Microglial Over-Activation In Vitro
- PMID: 25898934
- PMCID: PMC11486292
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-015-0195-5
Resveratrol Rescues the Impairments of Hippocampal Neurons Stimulated by Microglial Over-Activation In Vitro
Abstract
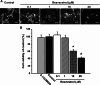
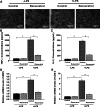
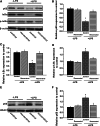
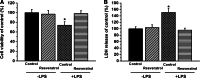
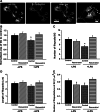
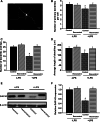
Resveratrol is a naturally occurring phytoalexin found in red grapes, and believed to have neuroprotective, anti-oxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects. But little is known about its effect on the neural impairments induced by microglial over-activation, which leads to neuroinflammation and multiple pathophysiological damages. In this study, we aimed to investigate the protective effects of resveratrol on the impairments of neural development by microglial over-activation insult. The results indicated that resveratrol inhibited the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-dependent release of cytokines from activated microglia and LPS-dependent changes in NF-κB signaling pathway. Conditioned medium (CM) from activated microglia treated by resveratrol directly protected primary cultured hippocampal neurons against LPS-CM-induced neuronal death, and restored the inhibitory effects of LPS-CM on dendrite sprouting and outgrowth. Finally, neurons cultured in CM from LPS-stimulated microglia treated by resveratrol exhibited increased spine density compared to those without resveratrol treatment. Our findings support that resveratrol inhibits microglial over-activation and alleviates neuronal injuries induced by microglial activation. Our study suggests the use of resveratrol as an alternative intervention approach that could prevent further neuronal insults.
Keywords: Hippocampal neuron; LPS; Microglia; NF-κB; Resveratrol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors (Feng Wang, Na Cui, Lijun Yang, Lin Shi, Qian Li, Gengshen Zhang, Jianliang Wu, Jun Zheng, and Baohua Jiao) declare there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
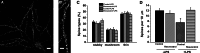
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

