Incidence and risk factors for falling in patients after total knee arthroplasty compared to healthy elderly individuals
- PMID: 25901101
- PMCID: PMC4404524
Incidence and risk factors for falling in patients after total knee arthroplasty compared to healthy elderly individuals
Abstract
Background: It is possible that patients who have undergone total knee arthroplasty (TKA) are at a high risk of falling. However, there are insufficient data to confirm the incidence and risk factors for falling in patients after TKA compared with healthy elderly counterparts. The purpose of this study was to elucidate the incidence and risk factors for falling in patients after TKA compared to the age- and gender-matched healthy elderly.
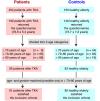
Methods: Subjects who underwent TKA consisted of 252 patients over 60 years of age. Controls were 150 healthy elderly individuals over 60 years of age living independently in the community. A self-administered questionnaire was mailed to patients after TKA and a similar questionnaire was distributed to the controls by investigators during the town-sponsored healthy aging program. The questionnaire included questions for ambulatory ability, functional status in daily living, knee pain, other joint pain and information on falls.
Results: Self-administered questionnares were returned by 192 of the 252 patients (76.1%) and 146 of the 150 controls (97.3%). Age and gender matching was performed for respondents between 70 and 80 years of age. There were 81 patients and 80 controls who fulfilled the inclusion criteria, and all of them agreed to participate. In the previous year, 34 of the 81 patients (38.2%) fell. The incidence of falls was significantly higher in patients than controls (23.8%, P = 0.041). In controls, ability to stand up from a chair without using the arms and restriction from joining social activities due to knee pain showed the strongest association with recent falls. In patients, self-reported kyphosis showed the strongest association with recent falls.
Conclusion: Patients after TKA are more likely to fall than the general Japanese population. Kyphosis showed the strongest association with recent falls in patients after TKA, which was different from the results obtained in the healthy elderly.
Keywords: elderly; falling; fractures; risk factor; total knee arthroplasty.
Figures
References
-
- Michel JP , Hoffmeyer P , Klopfenstein C , Bruchez M , Grab B , d’Epinay CL . Prognosis of functional recovery 1 year after hip fracture: typical patient profiles through cluster analysis. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2000; 55: M508-15. . - PubMed
-
- Koot VC , Peeters PH , de Jong JR , Clevers GJ , van der Werken C . Functional results after treatment of hip fracture: a multicentre, prospective study in 215 patients. Eur J Surg. 2000; 166: 480-5. . - PubMed
-
- Heikkinen T , Jalovaara P . Four or twelve months' follow-up in the evaluation of functional outcome after hip fracture surgery?. Scand J Surg. 2005; 94: 59-66. . - PubMed
-
- Levinger P , Menz HB , Wee E , Feller JA , Bartlett JR , Bergman NR . Physiological risk factors for falls in people with knee osteoarthritis before and early after knee replacement surgery. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011; 19: 1082-9. . - PubMed
-
- Arden NK , Crozier S , Smith H , Anderson F , Edwards C , Raphael H .Knee pain, knee osteoarthritis, and the risk of fracture. Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 55: 610-5. . - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources