Effects of kampo formulas on the progression of hypercholesterolemia and Fatty liver induced by high-cholesterol diet in rats
- PMID: 25901102
- PMCID: PMC4404525
Effects of kampo formulas on the progression of hypercholesterolemia and Fatty liver induced by high-cholesterol diet in rats
Abstract
Background: Bofutsushosan is a well known Kampo, traditional Japanese medicine, based on ancient Chinese medicine mainly used in the treatment of hypercholesterolemia in Japan. We selected two Kampo formulas, Boiogito and Keishibukuryogan mainly used in the treatment of hypercholesterolemia in China to compare with Bofutsushosan and cholesterol absorption inhibitor ezetimibe.
Methods: Hypercholesterolemia and fatty liver were induced by high cholesterol (containing 2% cholesterol and 0.5% cholic acid) diet in male Wistar rats for 6 and 12 weeks. Kampo formulas Boiogito, Bofutsushosan, Keishibukuryogan and ezetimibe were added to the high-cholesterol diet, respectively. After 6 and 12 weeks, body and liver weights, blood chemistry, cholesterol concentrations, fat-related and inflammatory-related factors were examined.
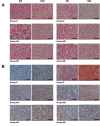
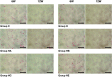
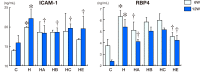
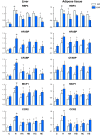
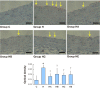
Results: High-cholesterol diet increased body and liver weights, and serum cholesterol concentrations. Boiogito and ezetimibe improved them. Serum ICAM-1 and RBP4 were increased in the high cholesterol diet group. Boiogito and ezetimibe improved them too. In the histological examinations of liver and adipose tissues, we observed a significant improvement after treatment. Immunostaining expression of ICAM-1 in aorta was improved by Boiogito, Bofutsushosan, Keishibukuryogan and ezetimibe. The mRNA expression of RBP4, HFABP, CFABP, MCP1 and CCR2 in liver and adipose tissue were decreased by Boiogito and ezetimibe.
Conclusion: Boiogito has a protective effect on the progression of hypercholesterolemia and fatty liver induced by high-cholesterol diet in rats and more effective than Bofutsushosan and Keishibukuryogan. The lipid-lowering effect of Boiogito is not stronger than ezetimibe. But the anti-inflammatory (MCP1, CCR2) and anti-arteriosclerotic (ICAM-1) effects of Boiogito are more potent than ezetimibe.
Keywords: Bofutsushosan; Boiogito; Keishibukuryogan; fatty liver; hypercholesterolemia.
Figures
References
-
- Roffi M , Brandle M , Robbins MA , Mukherjee D . Current perspectives on coronary revascularization in the diabetic patient. Indian Heart J. 2007; 59: 124-36. . - PubMed
-
- Angulo P , Lindor KD . Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002; 17Suppl: S186-90. . - PubMed
-
- Marchesini G , Moscatiello S , Di Domizio S , Forlani G . Obesity-associated liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008; 93 (11Suppl 1): S74-80. . - PubMed
-
- Targher G , Marra F , Marchesini G . Increased risk of cardiovascular disease in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: causal effect or epiphenomenon?. Diabetologia. 2008; 51: 1947-53. . - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
