Fascin-1 knock-down of human glioma cells reduces their microvilli/filopodia while improving their susceptibility to lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity
- PMID: 25901196
- PMCID: PMC4399091
Fascin-1 knock-down of human glioma cells reduces their microvilli/filopodia while improving their susceptibility to lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity
Abstract
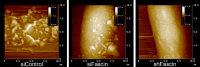
Cancer cells derived from Glioblastoma multiforme possess membranous protrusions allowing these cells to infiltrate surrounding tissue, while resisting lymphocyte cytotoxicity. Microvilli and filopodia are supported by actin filaments cross-linked by fascin. Fascin-1 was genetically silenced within human U251 glioma cells; these knock-down glioma cells lost their microvilli/filopodia. The doubling time of these fascin-1 knock-down cells was doubled that of shRNA control U251 cells. Fascin-1 knock-down cells lost their transmigratory ability responding to interleukin-6 or insulin-like growth factor-1. Fascin-1 silenced U251 cells were more easily killed by cytolytic lymphocytes. Fascin-1 knock-down provides unique opportunities to augment glioma immunotherapy by simultaneously targeting several key glioma functions: like cell transmigration, cell division and resisting immune responses.
Keywords: CTL; Fascin-1; filopodia; glioblastoma; microvilli; shRNA.
Figures






References
-
- Smyth MJ, Strobl SL, Young HA, Ortaldo JR, Ochoa AC. Regulation of lymphokine-activated killer activity and pore-forming protein gene expression in human peripheral blood CD8+ T lymphocytes. Inhibition by transforming growth factor-beta. J Immunol. 1991;146:3289–3297. - PubMed
-
- Wischhusen J, Friese MA, Mittelbronn M, Meyermann R, Weller M. HLA-E protects glioma cells from NKG2D-mediated immune responses in vitro: implications for immune escape in vivo. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2005;64:523–528. - PubMed
