Surface tension in human pathophysiology and its application as a medical diagnostic tool
- PMID: 25901295
- PMCID: PMC4401165
- DOI: 10.15171/bi.2015.06
Surface tension in human pathophysiology and its application as a medical diagnostic tool
Abstract
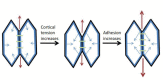
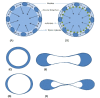
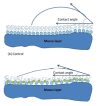
Introduction: Pathological features of disease appear to be quite different. Despite this diversity, the common feature of various disorders underlies physicochemical and biochemical factors such as surface tension. Human biological fluids comprise various proteins and phospholipids which are capable of adsorption at fluid interfaces and play a vital role in the physiological function of human organs. Surface tension of body fluids correlates directly to the development of pathological states.
Methods: In this review, the variety of human diseases mediated by the surface tension changes of biological phenomena and the failure of biological fluids to remain in their native state are discussed.
Results: Dynamic surface tension measurements of human biological fluids depend on various parameters such as sex, age and changes during pregnancy or certain disease. It is expected that studies of surface tension behavior of human biological fluids will provide additional information and might become useful in medical practice. Theoretical background on surface tension measurement and surface tension values of reference fluids obtained from healthy and sick patients are depicted.
Conclusion: It is well accepted that no single biomarker will be effective in clinical diagnosis. The surface tension measurement combined with routine lab tests may be a novel non-invasive method which can not only facilitate the discovery of diagnostic models for various diseases and its severity, but also be a useful tool for monitoring treatment efficacy. We therefore expect that studies of surface tension behavior of human biological fluids will provide additional useful information in medical practice.
Keywords: Biological fluid; Interfacial tension; Medical diagnosis; Pathological disease.
Similar articles
-
Studies on the application of dynamic surface tensiometry of serum and cerebrospinal liquid for diagnostics and monitoring of treatment in patients who have rheumatic, neurological or oncological diseases.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2000 May 24;86(1-2):1-38. doi: 10.1016/s0001-8686(00)00031-2. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2000. PMID: 10798349 Review.
-
Interfacial tension of some biological fluids: a comparative study.J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1981 May;19(5):267-71. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1981.19.5.267. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1981. PMID: 7264568
-
Evaluation of the Effect of the Volume Throughput and Maximum Flux of Low-Surface-Tension Fluids on Bacterial Penetration of 0.2 Micron-Rated Filters during Process-Specific Filter Validation Testing.PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2015 Mar-Apr;69(2):307-16. doi: 10.5731/pdajpst.2015.01026. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2015. PMID: 25868996
-
[Precise application of Traditional Chinese Medicine in minimally-invasive techniques].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2018 Jun 25;31(6):493-496. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0034.2018.06.001. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2018. PMID: 29945400 Chinese.
-
Advances in the design of fasted state simulating intestinal fluids: FaSSIF-V3.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Aug;94:229-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.05.015. Epub 2015 May 29. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015. PMID: 26032292 Review.
Cited by
-
Water in the human body: An anesthesiologist's perspective on the connection between physicochemical properties of water and physiologic relevance.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2017 Dec 27;26:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2017.12.007. eCollection 2018 Feb. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2017. PMID: 29904607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A ventilated perfused lung model platform to dissect the response of the lungs to viral infection.Trends Biotechnol. 2025 Jul;43(7):1714-1742. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2025.03.012. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Trends Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40280814
-
Microfluidic system for screening disease based on physical properties of blood.Bioimpacts. 2020;10(3):141-150. doi: 10.34172/bi.2020.18. Epub 2019 May 22. Bioimpacts. 2020. PMID: 32793436 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of spray and aerosol from respiratory releases: theoretical estimates for insight on viral transmission.Proc Math Phys Eng Sci. 2021 Jan;477(2245):20200584. doi: 10.1098/rspa.2020.0584. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Proc Math Phys Eng Sci. 2021. PMID: 33633490 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of food additives, artificial sweeteners and domestic hygiene products on the human gut microbiome and its fibre fermentation capacity.Eur J Nutr. 2020 Oct;59(7):3213-3230. doi: 10.1007/s00394-019-02161-8. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Eur J Nutr. 2020. PMID: 31853641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Castner DG, Ratner BD. Biomedical surface science: Foundations to frontiers. Surf Sci. 2002;500:28–60. doi: 10.1016/S0039-6028(01)01587-4. - DOI
-
- Kazakov VN, Vozianov AF, Sinyachenko OV, Trukhin DV, Kovalchuk VI, Pison U. Studies on the application of dynamic surface tensiometry of serum and cerebrospinal liquid for diagnostics and monitoring of treatment in patients who have rheumatic, neurological or oncological diseases. Adv Colloid Int Sci. 2000;86:1–38. doi: 10.1016/S0001-8686(00)00031-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Depalma RG. Surface forces in biological material; measurement of surface tension by drop volume. J Surg Res. 1967;7:317–322. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous