Self-Reported Reproductive Tract Infections and Ultrasound Diagnosed Uterine Fibroids in African-American Women
- PMID: 25901468
- PMCID: PMC4490779
- DOI: 10.1089/jwh.2014.5051
Self-Reported Reproductive Tract Infections and Ultrasound Diagnosed Uterine Fibroids in African-American Women
Abstract
Background: For decades, it has been hypothesized that reproductive tract infections (RTIs) are risk factors for uterine fibroids. However, only two recent studies have been conducted. We aimed to investigate the relationship between RTIs and fibroids in a large study using ultrasound screening for fibroids.
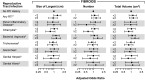
Methods: We used cross-sectional enrollment data from African American women ages 23-34 years with no previous fibroid diagnosis. RTI history was measured by self-report and fibroid status by standardized ultrasound. Secondary fibroid outcomes were size, number, and total volume. Age- and multivariable-adjusted logistic regression were used to estimate odds ratios (ORs).
Results: In total, 1,656 women were included; 22% had fibroids. Bacterial vaginosis (BV) was associated with a 21% increased odds of fibroids [aOR 1.21, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.93-1.58]. Chlamydia infection and pelvic inflammatory disease were associated with a 38% (aOR 0.62, 95% CI 0.40-0.97) and a 46% (aOR 0.54, 95% CI 0.25-1.17) reduced odds of having two or more fibroids, respectively. Those with a previous BV diagnosis had a 47% increased odds of having 2 or more fibroids (aOR 1.47, 95% CI 0.98-2.21) and a 41% increased odds of having a larger total fibroid volume (aOR 1.41, 95% CI 0.98-2.04).
Conclusions: Our study was the first to explore the relationship between RTIs and fibroid size, number, and total volume. There appeared to be no strong associations between self-reported RTIs and fibroids. Studies using serology, a biochemical measure of past infection, are needed to better investigate associations between RTIs and fibroids.
Figures
References
-
- Stewart EA. Uterine fibroids. Lancet 2001;357:293–298 - PubMed
-
- Baird D, Dunson DB, Hill MC, Cousins D, Schectman JM. High cumulative incidence of uterine leiomyoma in black and white women: Ultrasound evidence. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;188:100–107 - PubMed
-
- Pritts EA, Parker WH, Olive DL. Fibroids and infertility: An updated systematic review of the evidence. Fertil Steril 2009;91:1215–1223 - PubMed
-
- Lippman SA, Warner M, Samuels S, Olive D, Vercellini P, Eskenazi B. Uterine fibroids and gynecologic pain symptoms in a population-based study. Fertil Steril 2003;80:1488–1494 - PubMed
-
- Wegienka G, Baird DD, Hertz-Picciotto I, et al. Self-reported heavy bleeding associated with uterine leiomyomata. Obstet Gynecol 2003;101:431–437 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

