Formin 1 Regulates Ectoplasmic Specialization in the Rat Testis Through Its Actin Nucleation and Bundling Activity
- PMID: 25901598
- PMCID: PMC4511136
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2015-1161
Formin 1 Regulates Ectoplasmic Specialization in the Rat Testis Through Its Actin Nucleation and Bundling Activity
Abstract
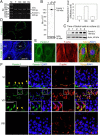
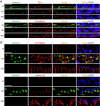
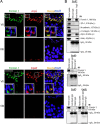
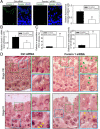
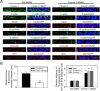
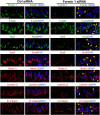
During spermatogenesis, developing spermatids and preleptotene spermatocytes are transported across the adluminal compartment and the blood-testis barrier (BTB), respectively, so that spermatids line up near the luminal edge to prepare for spermiation, whereas preleptotene spermatocytes enter the adluminal compartment to differentiate into late spermatocytes to prepare for meiosis I/II. These cellular events involve actin microfilament reorganization at the testis-specific, actin-rich Sertoli-spermatid and Sertoli-Sertoli cell junction called apical and basal ectoplasmic specialization (ES). Formin 1, an actin nucleation protein known to promote actin microfilament elongation and bundling, was expressed at the apical ES but limited to stage VII of the epithelial cycle, whereas its expression at the basal ES/BTB stretched from stage III to stage VI, diminished in stage VII, and was undetectable in stage VIII tubules. Using an in vitro model of studying Sertoli cell BTB function by RNA interference and biochemical assays to monitor actin bundling and polymerization activity, a knockdown of formin 1 in Sertoli cells by approximately 70% impeded the tight junction-permeability function. This disruptive effect on the tight junction barrier was mediated by a loss of actin microfilament bundling and actin polymerization capability mediated by changes in the localization of branched actin-inducing protein Arp3 (actin-related protein 3), and actin bundling proteins Eps8 (epidermal growth factor receptor pathway substrate 8) and palladin, thereby disrupting cell adhesion. Formin 1 knockdown in vivo was found to impede spermatid adhesion, transport, and polarity, causing defects in spermiation in which elongated spermatids remained embedded into the epithelium in stage IX tubules, mediated by changes in the spatiotemporal expression of Arp3, Eps8, and palladin. In summary, formin 1 is a regulator of ES dynamics.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transport of germ cells across the seminiferous epithelium during spermatogenesis-the involvement of both actin- and microtubule-based cytoskeletons.Tissue Barriers. 2016 Nov 28;4(4):e1265042. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2016.1265042. eCollection 2016. Tissue Barriers. 2016. PMID: 28123928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Actin-bundling protein plastin 3 is a regulator of ectoplasmic specialization dynamics during spermatogenesis in the rat testis.FASEB J. 2015 Sep;29(9):3788-805. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-267997. Epub 2015 Jun 5. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 26048141 Free PMC article.
-
Fascin 1 is an actin filament-bundling protein that regulates ectoplasmic specialization dynamics in the rat testis.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Nov 1;307(9):E738-53. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00113.2014. Epub 2014 Aug 26. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 25159326 Free PMC article.
-
Palladin is a regulator of actin filament bundles at the ectoplasmic specialization in adult rat testes.Endocrinology. 2013 May;154(5):1907-20. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-2269. Epub 2013 Apr 1. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23546604 Free PMC article.
-
Plastins regulate ectoplasmic specialization via its actin bundling activity on microfilaments in the rat testis.Asian J Androl. 2016 Sep-Oct;18(5):716-22. doi: 10.4103/1008-682X.166583. Asian J Androl. 2016. PMID: 26608945 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transport of germ cells across the seminiferous epithelium during spermatogenesis-the involvement of both actin- and microtubule-based cytoskeletons.Tissue Barriers. 2016 Nov 28;4(4):e1265042. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2016.1265042. eCollection 2016. Tissue Barriers. 2016. PMID: 28123928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell polarity, cell adhesion, and spermatogenesis: role of cytoskeletons.F1000Res. 2017 Aug 25;6:1565. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.11421.1. eCollection 2017. F1000Res. 2017. PMID: 28928959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formins: Actin nucleators that regulate cytoskeletal dynamics during spermatogenesis.Spermatogenesis. 2015 Jun 29;5(2):e1066476. doi: 10.1080/21565562.2015.1066476. eCollection 2015 May-Aug. Spermatogenesis. 2015. PMID: 26413414 Free PMC article.
-
Rab27a co-ordinates actin-dependent transport by controlling organelle-associated motors and track assembly proteins.Nat Commun. 2020 Jul 13;11(1):3495. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17212-6. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32661310 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear protein FNBP4: A novel inhibitor of non-diaphanous formin FMN1-mediated actin cytoskeleton dynamics.J Biol Chem. 2025 Jun;301(6):108550. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108550. Epub 2025 Apr 30. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40316024 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Franca LR, Auharek SA, Hess RA, Dufour JM, Hinton BT. Blood-tissue barriers: Morphofunctional and immunological aspects of the blood-testis and blood-epididymal barriers. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;763:237–259. - PubMed
-
- Pelletier RM. The blood-testis barrier: the junctional permeability, the proteins and the lipids. Prog Histochem Cytochem. 2011;46:49–127. - PubMed
-
- Hess RA, de Franca LR. Spermatogenesis and cycle of the seminiferous epithelium. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;636:1–15. - PubMed
-
- de Kretser DM, Kerr JB. The cytology of the testis. In: Knobil E, Neill JB, Ewing LL, Greenwald GS, Markert CL, Pfaff DW, eds. The Physiology of Reproduction. Vol 1 New York: Raven Press; 1988:837–932.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

