CCN5 attenuates profibrotic phenotypes of fibroblasts through the Smad6-CCN2 pathway: Potential role in epidural fibrosis
- PMID: 25901787
- PMCID: PMC4494601
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2190
CCN5 attenuates profibrotic phenotypes of fibroblasts through the Smad6-CCN2 pathway: Potential role in epidural fibrosis
Abstract
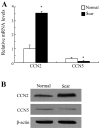
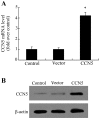
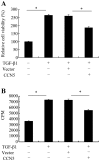
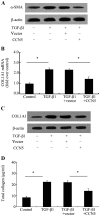
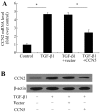
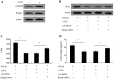
Epidural fibrosis is characterized by the development of dense and thick scar tissue adjacent to the dural mater and ranked as the major contributor for post-operative pain recurrence after laminectomy or discectomy. Recently, CCN5 exhibited an inhibitory effect on connective tissue growth factor (CTGF)/CCN2 (a critical regulator for fibrotic disease)‑mediated fibrogenesis. However, its function in epidural fibrosis and the underlying mechanisms involved remain to be determined. In this study, an obvious downregulation of CCN5 was observed in scar tissues from laminectomized rats, concomitant with a marked upregulation of CCN2, suggesting a potential negative regulatory role of CCN5 in fibrogenesis. Furthermore, CCN5 overexpression notably mitigated transforming growth factor‑β1-enhanced fibroblast viability and proliferation. Of note, CCN5 upregulation inhibited the switch of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts as its overexpression abrogated the expression of the myofibroblast marker, α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA). CCN5 upregulation also reduced an increase in collagen type I, α1 (COL1A1) and total collagen concentrations. Additionally, CCN5 over-expression decreased CCN2 expression and increased Smad6 phosphorylation. Mechanism analysis revealed that blocking Smad6 signaling significantly ameliorated the inhibitory effect of CCN5 on the CCN2 levels, accompanied by the reduction in cell proliferation and collagen production. These results confirm that CCN5 exerts an anti-fibrotic function by regulating the Smad6-CCN2 pathway, thereby indicating a potential approach for ameliorating epidural fibrosis after laminectomy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CCN2 and CCN5 exerts opposing effect on fibroblast proliferation and transdifferentiation induced by TGF-β.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015 Nov;42(11):1207-19. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12470. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26218313
-
CCN5 overexpression inhibits profibrotic phenotypes via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in lung fibroblasts isolated from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and in an in vivo model of lung fibrosis.Int J Mol Med. 2014 Feb;33(2):478-86. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1565. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Int J Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24276150
-
[Effects of CCN5 overexpression on the expression of alpha-SMA and collagen I in hepatic stellate cells and its mechanism].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2013 Sep;29(5):411-5. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24386815 Chinese.
-
Role of CCN5 (WNT1 inducible signaling pathway protein 2) in pancreatic islets.J Diabetes. 2017 May;9(5):462-474. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12507. Epub 2016 Dec 26. J Diabetes. 2017. PMID: 27863006 Review.
-
Metabolic Effects of CCN5/WISP2 Gene Deficiency and Transgenic Overexpression in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 14;22(24):13418. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413418. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948212 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacotherapies to prevent epidural fibrosis after laminectomy: a systematic review of in vitro and in vivo animal models.Spine J. 2023 Oct;23(10):1471-1484. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2023.05.007. Epub 2023 May 13. Spine J. 2023. PMID: 37187251 Free PMC article.
-
CCN5-Derived Peptide Ameliorates Liver Fibrosis in Mice through Inhibiting the ERK1/2 and PI3K Signaling Pathways.ACS Omega. 2025 Apr 1;10(14):14221-14228. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c00128. eCollection 2025 Apr 15. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40256553 Free PMC article.
-
CCN proteins: opportunities for clinical studies-a personal perspective.J Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Jun;17(2):333-352. doi: 10.1007/s12079-023-00761-y. Epub 2023 May 17. J Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37195381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CCN5/WISP2 and metabolic diseases.J Cell Commun Signal. 2018 Mar;12(1):309-318. doi: 10.1007/s12079-017-0437-z. Epub 2017 Dec 15. J Cell Commun Signal. 2018. PMID: 29247377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Honokiol protects against epidural fibrosis by inhibiting fibroblast proliferation and extracellular matrix overproduction in rats post‑laminectomy.Int J Mol Med. 2020 Dec;46(6):2057-2068. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4765. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33125121 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bottegaro NB, Kos J, Pirkic B, et al. Reduction of epidural fibrosis after laminectomy in rabbits by omental free graft. Vet Med. 2013;58:25–31.
-
- Guo JD, Hou SX, Li L, et al. Laminectomy and extraction of nucleus pulposus for treatment of lumbar disc herniation: effect evaluation of over 10-year-followed-up. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2013;26:24–28. In Chinese. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

