Highly compressible 3D periodic graphene aerogel microlattices
- PMID: 25902277
- PMCID: PMC4421818
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms7962
Highly compressible 3D periodic graphene aerogel microlattices
Abstract
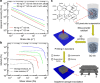
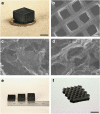
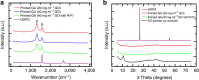
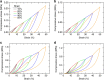
Graphene is a two-dimensional material that offers a unique combination of low density, exceptional mechanical properties, large surface area and excellent electrical conductivity. Recent progress has produced bulk 3D assemblies of graphene, such as graphene aerogels, but they possess purely stochastic porous networks, which limit their performance compared with the potential of an engineered architecture. Here we report the fabrication of periodic graphene aerogel microlattices, possessing an engineered architecture via a 3D printing technique known as direct ink writing. The 3D printed graphene aerogels are lightweight, highly conductive and exhibit supercompressibility (up to 90% compressive strain). Moreover, the Young's moduli of the 3D printed graphene aerogels show an order of magnitude improvement over bulk graphene materials with comparable geometric density and possess large surface areas. Adapting the 3D printing technique to graphene aerogels realizes the possibility of fabricating a myriad of complex aerogel architectures for a broad range of applications.
Figures

References
-
- Geim A. K. & Novoselov K. S. The rise of graphene. Nature Mater. 6, 183–191 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Li D. & Kaner R. B. Graphene-based materials. Science 320, 1170–1171 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Geim A. K. Graphene: status and prospects. Science 324, 1530–1534 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Peigney A., Laurent C., Flahaut E., Bacsa R. R. & Rousset A. Specific surface area of carbon nanotubes and bundles of carbon nanotubes. Carbon 39, 507–514 (2001).
-
- Lee C., Wei X., Kysar J. W. & Hone J. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 321, 385–388 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

