Head-to-head antisense transcription and R-loop formation promotes transcriptional activation
- PMID: 25902512
- PMCID: PMC4426458
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1421197112
Head-to-head antisense transcription and R-loop formation promotes transcriptional activation
Abstract
The mechanisms used by antisense transcripts to regulate their corresponding sense mRNAs are not fully understood. Herein, we have addressed this issue for the vimentin (VIM) gene, a member of the intermediate filament family involved in cell and tissue integrity that is deregulated in different types of cancer. VIM mRNA levels are positively correlated with the expression of a previously uncharacterized head-to-head antisense transcript, both transcripts being silenced in colon primary tumors concomitant with promoter hypermethylation. Furthermore, antisense transcription promotes formation of an R-loop structure that can be disfavored in vitro and in vivo by ribonuclease H1 overexpression, resulting in VIM down-regulation. Antisense knockdown and R-loop destabilization both result in chromatin compaction around the VIM promoter and a reduction in the binding of transcriptional activators of the NF-κB pathway. These results are the first examples to our knowledge of R-loop-mediated enhancement of gene expression involving head-to-head antisense transcription at a cancer-related locus.
Keywords: DNA methylation; R loop; antisense transcription; nucleosome occupancy; vimentin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
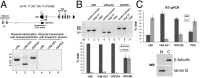



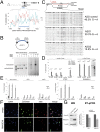
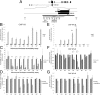
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

