The Cancer Genome Atlas Analysis Predicts MicroRNA for Targeting Cancer Growth and Vascularization in Glioblastoma
- PMID: 25903473
- PMCID: PMC4817797
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2015.72
The Cancer Genome Atlas Analysis Predicts MicroRNA for Targeting Cancer Growth and Vascularization in Glioblastoma
Abstract
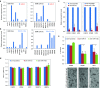
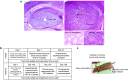
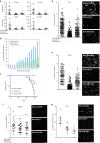
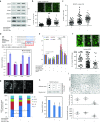
Using in silico analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), we identified microRNAs associated with glioblastoma (GBM) survival, and predicted their functions in glioma growth and progression. Inhibition of two "risky" miRNAs, miR-148a and miR-31, in orthotopic xenograft GBM mouse models suppressed tumor growth and thereby prolonged animal survival. Intracranial tumors treated with uncomplexed miR-148a and miR-31 antagomirs exhibited reduced proliferation, stem cell depletion, and normalized tumor vasculature. Growth-promoting functions of these two miRNAs were, in part, mediated by the common target, the factor inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (FIH1), and the downstream pathways involving hypoxia-inducible factor HIF1α and Notch signaling. Therefore, miR-31 and miR-148a regulate glioma growth by maintaining tumor stem cells and their niche, and providing the tumor a way to activate angiogenesis even in a normoxic environment. This is the first study that demonstrates intratumoral uptake and growth-inhibiting effects of uncomplexed antagomirs in orthotopic glioma.
Figures



References
-
- Chan, JA, Krichevsky, AM and Kosik, KS (2005). MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 65: 6029–6033. - PubMed
-
- Hayashita, Y, Osada, H, Tatematsu, Y, Yamada, H, Yanagisawa, K, Tomida, S et al. (2005). A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res 65: 9628–9632. - PubMed
-
- Janssen, HL, Reesink, HW, Lawitz, EJ, Zeuzem, S, Rodriguez-Torres, M, Patel, K et al. (2013). Treatment of HCV infection by targeting microRNA. N Engl J Med 368: 1685–1694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

