MALDI FTICR IMS of Intact Proteins: Using Mass Accuracy to Link Protein Images with Proteomics Data
- PMID: 25904064
- PMCID: PMC4442642
- DOI: 10.1007/s13361-015-1147-5
MALDI FTICR IMS of Intact Proteins: Using Mass Accuracy to Link Protein Images with Proteomics Data
Abstract
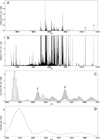
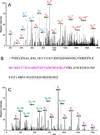
MALDI imaging mass spectrometry is a highly sensitive and selective tool used to visualize biomolecules in tissue. However, identification of detected proteins remains a difficult task. Indirect identification strategies have been limited by insufficient mass accuracy to confidently link ion images to proteomics data. Here, we demonstrate the capabilities of MALDI FTICR MS for imaging intact proteins. MALDI FTICR IMS provides an unprecedented combination of mass resolving power (~75,000 at m/z 5000) and accuracy (<5ppm) for proteins up to ~12kDa, enabling identification based on correlation with LC-MS/MS proteomics data. Analysis of rat brain tissue was performed as a proof-of-concept highlighting the capabilities of this approach by imaging and identifying a number of proteins including N-terminally acetylated thymosin β(4) (m/z 4,963.502, 0.6ppm) and ATP synthase subunit ε (m/z 5,636.074, -2.3ppm). MALDI FTICR IMS was also used to differentiate a series of oxidation products of S100A8 (m/z 10,164.03, -2.1ppm), a subunit of the heterodimer calprotectin, in kidney tissue from mice infected with Staphylococcus aureus. S100A8 - M37O/C42O(3) (m/z 10228.00, -2.6ppm) was found to co-localize with bacterial microcolonies at the center of infectious foci. The ability of MALDI FTICR IMS to distinguish S100A8 modifications is critical to understanding calprotectin's roll in nutritional immunity.
Figures
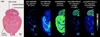



References
-
- Caprioli RM, Farmer TB, Gile J. Molecular imaging of biological samples: localization of peptides and proteins using MALDI-TOF MS. Anal Chem. 1997;69:4751–4760. - PubMed
-
- Nilsson A, Goodwin RJ, Shariatgorji M, Vallianatou T, Webborn PJ, Andren PE. Mass spectrometry imaging in drug development. Anal Chem. 2015;87:1437–1455. - PubMed
-
- Huang JT, Hannah-Qiuhua L, Szyszka R, Veselov V, Reed G, Wang X, et al. Molecular imaging of drug-eluting coronary stents: method development, optimization and selected applications. J Mass Spectrom. 2012;47:155–162. - PubMed
-
- Bhandari DR, Schott M, Rompp A, Vilcinskas A, Spengler B. Metabolite localization by atmospheric pressure high-resolution scanning microprobe matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging in whole-body sections and individual organs of the rove beetle Paederus riparius. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

