Reappraisal of the diagnostic and prognostic value of morning stiffness in arthralgia and early arthritis: results from the Groningen EARC, Leiden EARC, ESPOIR, Leiden EAC and REACH
- PMID: 25904188
- PMCID: PMC4445798
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-015-0616-3
Reappraisal of the diagnostic and prognostic value of morning stiffness in arthralgia and early arthritis: results from the Groningen EARC, Leiden EARC, ESPOIR, Leiden EAC and REACH
Abstract
Introduction: Morning stiffness is assessed daily in the diagnostic process of arthralgia and arthritis, but large-scale studies on the discriminative ability are absent. This study explored the diagnostic value of morning stiffness in 5,202 arthralgia and arthritis patients and the prognostic value in early rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
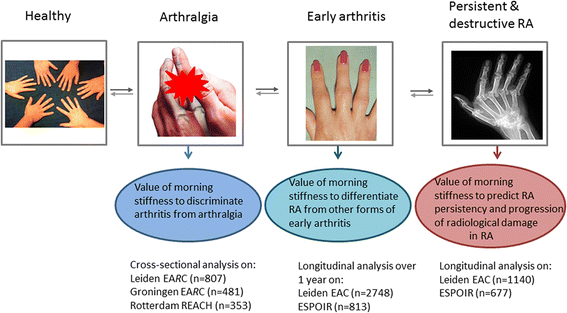
Methods: In arthralgia patients referred to the Early Arthritis Recognition Clinics (EARC) of Leiden (n = 807) and Groningen (n = 481) or included in the Rotterdam Early Arthritis Cohort (REACH) study (n = 353), the associations (cross-sectional analyses) between morning stiffness and presence of arthritis at physical examination were studied. In early arthritis patients, included in the Leiden Early Arthritis Clinic (EAC) (n = 2,748) and Evaluation et Suivi de POlyarthrites Indifférenciées Récentes (ESPOIR) (n = 813), associations with fulfilling the 2010-RA criteria after one year were assessed. In 2010-RA patients included in the EAC (n = 1,140) and ESPOIR (n = 677), association with the long-term outcomes of disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD)-free sustained remission and radiological progression were determined. Morning stiffness was defined as a duration ≥60 minutes; sensitivity analyses were performed for other definitions.
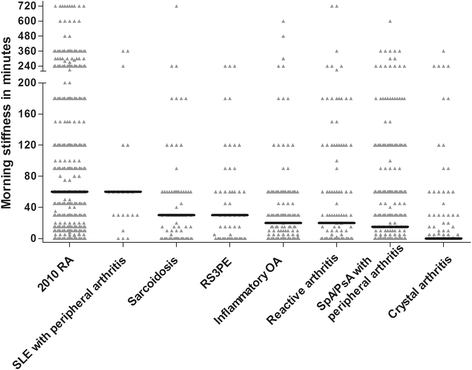
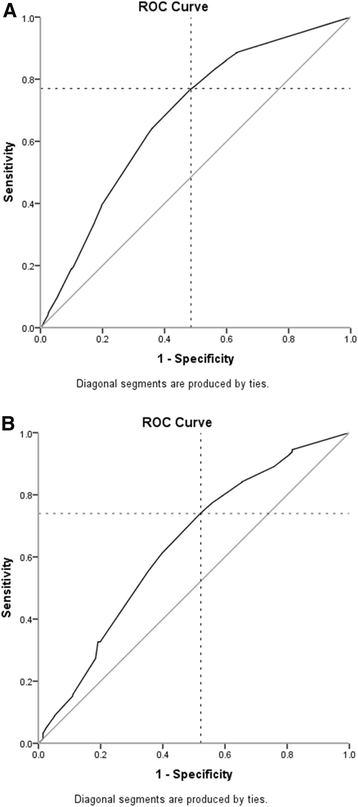
Results: In arthralgia, morning stiffness (≥60 minutes) associated with the presence of arthritis; Leiden EARC odds ratio (OR) 1.49 (95% CI 1.001 to 2.20), Groningen EARC OR 2.21 (1.33 to 3.69) and REACH OR 1.55 (0.97 to 2.47) but the areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUCs) were low (0.52, 0.57, 0.54). In early arthritis, morning stiffness was associated with 2010-RA independent of other predictors (Leiden EAC OR 1.72 (95% CI 1.31 to 2.25, AUC 0.68), ESPOIR OR 1.68 (1.03 to 2.74, AUC 0.64)). Duration of ≥30 minutes provided optimal discrimination for RA in early arthritis. Morning stiffness was not associated with radiological progression or DMARD-free sustained remission.
Conclusions: Morning stiffness in arthralgia and early arthritis is associated with arthritis and RA respectively. This supports the incorporation of morning stiffness in the diagnostic process.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluating relationships between symptom duration and persistence of rheumatoid arthritis: does a window of opportunity exist? Results on the Leiden early arthritis clinic and ESPOIR cohorts.Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 May;74(5):806-12. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206047. Epub 2015 Jan 5. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015. PMID: 25561360
-
Referring early arthritis patients within 6 weeks versus 12 weeks after symptom onset: an observational cohort study.Lancet Rheumatol. 2020 Jun;2(6):e332-e338. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30061-8. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 38273596
-
Prevalence of and predictive factors for sustained disease-modifying antirheumatic drug-free remission in rheumatoid arthritis: results from two large early arthritis cohorts.Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Aug;60(8):2262-71. doi: 10.1002/art.24661. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. PMID: 19644846
-
The importance of assessment and management of morning stiffness in Asian patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Recommendations from an expert panel.Int J Rheum Dis. 2016 Jan;19(1):30-7. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12755. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016. PMID: 26403254
-
EULAR definition of arthralgia suspicious for progression to rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Mar;76(3):491-496. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209846. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017. PMID: 27991858
Cited by
-
Delayed Treatment Acceleration in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Who Have Inadequate Response to Initial Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors: Data from the Corrona Registry.Am Health Drug Benefits. 2018 May;11(3):148-158. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2018. PMID: 29910846 Free PMC article.
-
Role of specialized pro-resolving mediators on inflammation, cardiometabolic health, disease progression, and quality of life after omega-3 PUFA supplementation and aerobic exercise training in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized 16-week, placebo-controlled interventional trial.F1000Res. 2023 Aug 7;12:942. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.138392.1. eCollection 2023. F1000Res. 2023. PMID: 38778807 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Risk Factors for Developing Rheumatoid Arthritis in Patients With Undifferentiated Arthritis and Inflammatory Arthralgia.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Jun 15;8:668898. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.668898. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34211986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contribution of tenosynovitis of small joints to the symptom morning stiffness in patients presenting with undifferentiated and rheumatoid arthritis.Scand J Rheumatol. 2020 May;49(3):181-185. doi: 10.1080/03009742.2019.1696404. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Scand J Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32181696 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between daily pain and affect in women with rheumatoid arthritis: lower optimism as a vulnerability factor.J Behav Med. 2018 Feb;41(1):12-21. doi: 10.1007/s10865-017-9874-7. Epub 2017 Jul 17. J Behav Med. 2018. PMID: 28718078 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wolfe F, Hawley DJ, Cathey MA. Clinical and health status measures over time: prognosis and outcome assessment in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1991;18:1290–7. - PubMed
-
- Hazes JM, Hayton R, Silman AJ. A reevaluation of the symptom of morning stiffness. J Rheumatol. 1993;20:1138–42. - PubMed
-
- Yazici Y, Erkan D, Peterson MG, Kagen LJ. Morning stiffness: how common is it and does it correlate with physician and patient global assessment of disease activity? J Rheumatol. 2001;28:1468–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

