Functional analysis and transcriptomic profiling of iPSC-derived macrophages and their application in modeling Mendelian disease
- PMID: 25904599
- PMCID: PMC4565503
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.305860
Functional analysis and transcriptomic profiling of iPSC-derived macrophages and their application in modeling Mendelian disease
Abstract
Rationale: An efficient and reproducible source of genotype-specific human macrophages is essential for study of human macrophage biology and related diseases.
Objective: To perform integrated functional and transcriptome analyses of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived macrophages (IPSDMs) and their isogenic human peripheral blood mononuclear cell-derived macrophage (HMDM) counterparts and assess the application of IPSDM in modeling macrophage polarization and Mendelian disease.
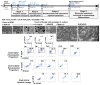
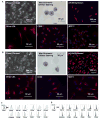
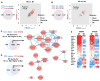
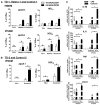
Methods and results: We developed an efficient protocol for differentiation of IPSDM, which expressed macrophage-specific markers and took up modified lipoproteins in a similar manner to HMDM. Like HMDM, IPSDM revealed reduction in phagocytosis, increase in cholesterol efflux capacity and characteristic secretion of inflammatory cytokines in response to M1 (lipopolysaccharide+interferon-γ) activation. RNA-Seq revealed that nonpolarized (M0) as well as M1 or M2 (interleukin-4) polarized IPSDM shared transcriptomic profiles with their isogenic HMDM counterparts while also revealing novel markers of macrophage polarization. Relative to IPSDM and HMDM of control individuals, patterns of defective cholesterol efflux to apolipoprotein A-I and high-density lipoprotein-3 were qualitatively and quantitatively similar in IPSDM and HMDM of patients with Tangier disease, an autosomal recessive disorder because of mutations in ATP-binding cassette transporter AI. Tangier disease-IPSDM also revealed novel defects of enhanced proinflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide stimulus.
Conclusions: Our protocol-derived IPSDM are comparable with HMDM at phenotypic, functional, and transcriptomic levels. Tangier disease-IPSDM recapitulated hallmark features observed in HMDM and revealed novel inflammatory phenotypes. IPSDMs provide a powerful tool for study of macrophage-specific function in human genetic disorders as well as molecular studies of human macrophage activation and polarization.
Keywords: cholesterol; genomics; induced pluripotent stem cells; inflammation; macrophages.
© 2015 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Yamanaka S. Induced pluripotent stem cells: Past, present, and future. Cell stem cell. 2012;10:678–684. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01-HL-111694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK-090505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL113147/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-HL-108636/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK090505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL108636/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL107643/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24-HL-107643/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-HG006398/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-113147/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006398/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

