High Viral Load and Respiratory Failure in Adults Hospitalized for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections
- PMID: 25904604
- PMCID: PMC7539363
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiv248
High Viral Load and Respiratory Failure in Adults Hospitalized for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections
Abstract
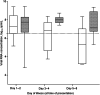
A prospective study among adults hospitalized for polymerase chain reaction-confirmed respiratory syncytial virus infections (n = 123) showed frequent occurrence of lower respiratory-tract complications causing respiratory insufficiency (52.8%), requirement for assisted ventilation (16.3%), and intensive care unit admission/death (12.2%). High viral RNA concentration was detected at time of hospitalization, including in patients who presented later than 2 days of illness (day 1-2, 7.29 ± 1.47; day 3-4, 7.28 ± 1.41; day 5-8, 6.66 ± 1.87 log10 copies/mL). RNA concentration was independently associated with risk of complications and respiratory insufficiency (adjusted odds ratio 1.40 per log10 copies/mL increase, 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.90; P = .034). Our data indicate the need and provide a basis for clinical research on antiviral therapy in this population.
Keywords: RSV; respiratory failure; viral load.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Lee N, Lui GC, Wong KT et al. . High morbidity and mortality in adults hospitalized for respiratory syncytial virus infections. Clin Infect Dis 2013; 57:1069–77. - PubMed
-
- Walsh EE, Peterson DR, Falsey AR. Is clinical recognition of respiratory syncytial virus infection in hospitalized elderly and high-risk adults possible? J Infect Dis 2007; 195:1046–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

