Impact of a low-glucose peritoneal dialysis regimen on fibrosis and inflammation biomarkers
- PMID: 25904773
- PMCID: PMC4406310
- DOI: 10.3747/pdi.2014.00125
Impact of a low-glucose peritoneal dialysis regimen on fibrosis and inflammation biomarkers
Abstract
Background: The impact of a low-glucose peritoneal dialysis (PD) regimen on biomarkers of peritoneal inflammation, fibrosis and membrane integrity remains to be investigated.
Methods: In a randomized, prospective study, 80 incident PD patients received either a low-glucose regimen comprising Physioneal (P), Extraneal (E) and Nutrineal (N) (Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Deerfield, IL, USA) (PEN group), or Dianeal (control group) for 12 months, after which both groups continued with Dianeal dialysis for 6 months. Serum and dialysate levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), decorin, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), interleukin-6 (IL-6), macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF), hyaluronan (HA), adiponectin, soluble-intracellular adhesion molecule (s-ICAM), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and P-selectin, and dialysate cancer antigen 125 (CA125), were measured after 12 and 18 months. This paper focuses on results after 12 months, when patients in the PEN group changed to glucose-based PD fluid (PDF).
Results: At the end of 12 months, effluent dialysate levels of CA125, decorin, HGF, IL-6, adiponectin and adhesion molecules were significantly higher in the PEN group compared to controls, but all decreased after patients switched to glucose-based PDF. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor level was lower in the PEN group but increased after changing to glucose-based PDF and was similar to controls at 18 months. Serum adiponectin level was higher in the PEN group at 12 months, but was similar in the 2 groups at 18 months. Body weight, residual renal function, ultrafiltration volume and total Kt/V did not differ between both groups. Dialysate-to-plasma creatinine ratio at 4 h was higher in the PEN group at 12 months and remained so after switching to glucose-based PDF.
Conclusion: Changes in the biomarkers suggest that the PEN PD regimen may be associated with better preservation of peritoneal membrane integrity and reduced systemic vascular endothelial injury.
Keywords: Amino acid; biocompatibility; icodextrin; pH neutral; peritoneal dialysis; peritoneal inflammation.
Copyright © 2015 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis.
Figures
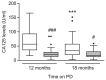
 ). Data are presented as median (horizontal line within box), 25th and 75th percentiles (bottom and top of the box respectively), and the lowest and highest values (bars), excluding outliers (•), the latter defined as values greater than 1.5 times the interquartile range above the third quartile or below the first quartile. Intra- and inter-group comparisons were analyzed with ANOVA. PD = peritoneal dialysis; CA = cancer antigen; PEN = Physioneal (P), Extraneal (E), Nutrineal (N); *** = p<0.001 (12 months vs 18 months in PEN Group); # = p<0.05; ### = p<0.001 (PEN vs control for the same time-point).
). Data are presented as median (horizontal line within box), 25th and 75th percentiles (bottom and top of the box respectively), and the lowest and highest values (bars), excluding outliers (•), the latter defined as values greater than 1.5 times the interquartile range above the third quartile or below the first quartile. Intra- and inter-group comparisons were analyzed with ANOVA. PD = peritoneal dialysis; CA = cancer antigen; PEN = Physioneal (P), Extraneal (E), Nutrineal (N); *** = p<0.001 (12 months vs 18 months in PEN Group); # = p<0.05; ### = p<0.001 (PEN vs control for the same time-point).
 ). Data are presented as median (horizontal line within box), 25th and 75th percentiles (bottom and top of the box respectively), and the lowest and highest values (bars), excluding outliers (•), the latter defined as values greater than 1.5 times the interquartile range above the third quartile or below the first quartile. Intra- and inter-group comparisons were analyzed with ANOVA. PEN = Physioneal (P), Extraneal (E), Nutrineal (N); PD = peritoneal dialysis; HGF = hepatocyte growth factor; VEGF = vascular endothelial growth factor; # = p<0.05 (PEN vs control for the same time-point).
). Data are presented as median (horizontal line within box), 25th and 75th percentiles (bottom and top of the box respectively), and the lowest and highest values (bars), excluding outliers (•), the latter defined as values greater than 1.5 times the interquartile range above the third quartile or below the first quartile. Intra- and inter-group comparisons were analyzed with ANOVA. PEN = Physioneal (P), Extraneal (E), Nutrineal (N); PD = peritoneal dialysis; HGF = hepatocyte growth factor; VEGF = vascular endothelial growth factor; # = p<0.05 (PEN vs control for the same time-point).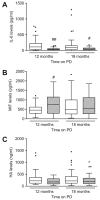
 ). Data are presented as median (horizontal line within box), 25th and 75th percentiles (bottom and top of the box respectively), and the lowest and highest values (bars), excluding outliers (•), the latter defined as values greater than 1.5 times the interquartile range above the third quartile or below the first quartile. Intra- and inter-group comparisons were analyzed with ANOVA. PEN = Physioneal (P), Extraneal (E), Nutrineal (N); PD = peritoneal dialysis; IL-6 = interleukin-6; MIF = macrophage migration inhibitory factor; HA = hyaluronan; # = p<0.05, ## = p<0.01 (PEN vs control for the same time-point).
). Data are presented as median (horizontal line within box), 25th and 75th percentiles (bottom and top of the box respectively), and the lowest and highest values (bars), excluding outliers (•), the latter defined as values greater than 1.5 times the interquartile range above the third quartile or below the first quartile. Intra- and inter-group comparisons were analyzed with ANOVA. PEN = Physioneal (P), Extraneal (E), Nutrineal (N); PD = peritoneal dialysis; IL-6 = interleukin-6; MIF = macrophage migration inhibitory factor; HA = hyaluronan; # = p<0.05, ## = p<0.01 (PEN vs control for the same time-point).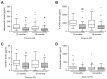
 ). Data are presented as median (horizontal line within box), 25th and 75th percentiles (bottom and top of the box respectively), and the lowest and highest values (bars), excluding outliers (•), the latter defined as values greater than 1.5 times the interquartile range above the third quartile or below the first quartile. Intra- and inter-group comparisons were analyzed with ANOVA. PEN = Physioneal (P), Extraneal (E), Nutrineal (N); PD = peritoneal dialysis; s-ICAM = soluble-intracellular adhesion molecule; VCAM-1 = vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; # = p<0.05; ## = p<0.01 (PEN vs control for the same time-point).
). Data are presented as median (horizontal line within box), 25th and 75th percentiles (bottom and top of the box respectively), and the lowest and highest values (bars), excluding outliers (•), the latter defined as values greater than 1.5 times the interquartile range above the third quartile or below the first quartile. Intra- and inter-group comparisons were analyzed with ANOVA. PEN = Physioneal (P), Extraneal (E), Nutrineal (N); PD = peritoneal dialysis; s-ICAM = soluble-intracellular adhesion molecule; VCAM-1 = vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; # = p<0.05; ## = p<0.01 (PEN vs control for the same time-point).Comment in
-
The solution to better preservation of the peritoneal membrane still lies hidden in the solution.Perit Dial Int. 2015 Mar-Apr;35(2):125-7. doi: 10.3747/pdi.2015.00032. Perit Dial Int. 2015. PMID: 25904771 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Williams JD, Craig KJ, Topley N, Von Ruhland C, Fallon M, Newman GR, et al. Morphologic changes in the peritoneal membrane of patients with renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 2002; 13:470–9. - PubMed
-
- Schalkwijk CG, Posthuma N, ten Brink HJ, ter Wee PM, Teerlink T. Induction of 1,2-dicarbonyl compounds, intermediates in the formation of advanced glycation end-products, during heat-sterilization of glucose-based peritoneal dialysis fluids. Perit Dial Int 1999; 19:325–33. - PubMed
-
- Witowski J, Wisniewska J, Korybalska K, Bender TO, Breborowicz A, Gahl GM, et al. Prolonged exposure to glucose degradation products impairs viability and function of human peritoneal mesothelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 2001; 12:2434–41. - PubMed
-
- Chan TM, Leung JK, Sun Y, Lai KN, Tsang RC, Yung S. Different effects of amino acid-based and glucose-based dialysate from peritoneal dialysis patients on mesothelial cell ultrastructure and function. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2003; 18:1086–94. - PubMed
-
- Ha H, Cha MK, Choi HN, Lee HB. Effects of peritoneal dialysis solutions on the secretion of growth factors and extracellular matrix proteins by human peritoneal mesothelial cells. Perit Dial Int 2002; 22:171–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

