Cognitive training enhances intrinsic brain connectivity in childhood
- PMID: 25904781
- PMCID: PMC4405549
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4517-14.2015
Cognitive training enhances intrinsic brain connectivity in childhood
Abstract
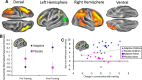
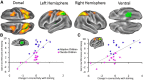
In human participants, the intensive practice of particular cognitive activities can induce sustained improvements in cognitive performance, which in some cases transfer to benefits on untrained activities. Despite the growing body of research examining the behavioral effects of cognitive training in children, no studies have explored directly the neural basis of these training effects in a systematic, controlled fashion. Therefore, the impact of training on brain neurophysiology in childhood, and the mechanisms by which benefits may be achieved, are unknown. Here, we apply new methods to examine dynamic neurophysiological connectivity in the context of a randomized trial of adaptive working memory training undertaken in children. After training, connectivity between frontoparietal networks and both lateral occipital complex and inferior temporal cortex was altered. Furthermore, improvements in working memory after training were associated with increased strength of neural connectivity at rest, with the magnitude of these specific neurophysiological changes being mirrored by individual gains in untrained working memory performance.
Keywords: Cognitive training; development; electrophysiology; magnetoencephalography; working memory.
Copyright © 2015 the authors 0270-6474/15/356277-07$15.00/0.
Figures



References
-
- Alloway TP, Gathercole SE, Kirkwood H, Elliott J. Evaluating the validity of the Automated Working Memory Assessment. Educational Psychology. 2008;28:725–734.
-
- Barnes JJ, Woolrich MW, Baker K, Colclough GL, Astle DE. Electrophysiological measures of resting state functional connectivity and their relationship with working memory capacity in childhood. Dev Sci. 2015 doi: 10.1111/desc.12297. doi: 10.1111/desc.12297. Advance online publication. - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
