The Implantable Pediatric Artificial Lung: Interim Report on the Development of an End-Stage Lung Failure Model
- PMID: 25905495
- PMCID: PMC4486510
- DOI: 10.1097/MAT.0000000000000230
The Implantable Pediatric Artificial Lung: Interim Report on the Development of an End-Stage Lung Failure Model
Abstract
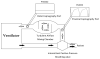
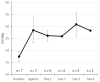
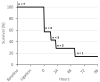
An implantable pediatric artificial lung (PAL) may serve as a bridge to lung transplantation for children with end-stage lung failure (ESLF); however, an animal model of pediatric lung failure is needed to evaluate the efficacy of PAL before it can enter clinical trials. The objective of this study was to assess ligation of the right pulmonary artery (rPA) as a model for pediatric ESLF. Seven lambs weighing 20-30 kg underwent rPA ligation and were recovered and monitored for up to 4 days. Intraoperatively, rPA ligation significantly increased physiologic dead space fraction (Vd/Vt; baseline = 48.6 ± 5.7%, rPA ligation = 60.1 ± 5.2%, p = 0.012), mean pulmonary arterial pressure (mPPA; baseline = 17.4 ± 2.2 mm Hg, rPA ligation = 28.5 ± 5.2 mm Hg, p < 0.001), and arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide (baseline = 40.4 ± 9.3 mm Hg, rPA ligation = 57.3 ± 12.7 mm Hg, p = 0.026). Of the seven lambs, three were unable to be weaned from mechanical ventilation postoperatively, three were successfully weaned but suffered cardiorespiratory failure within 4 days, and one survived all 4 days. All four animals that were successfully weaned from mechanical ventilation had persistent pulmonary hypertension (mPPA = 28.6 ± 2.2 mm Hg) and remained tachypneic (respiratory rate = 63 ± 21 min). Three of the four recovered lambs required supplemental oxygen. We conclude that rPA ligation creates the physiologic derangements commonly seen in pediatric ESLF and may be suitable for testing and implanting a PAL.
Figures
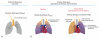
References
-
- Benden C, Edwards LB, Kucheryavaya AY, Christie JD, Dipchand AI, Dobbels F, Kirk R, Lund LH, Rahmel AO, Yusen RD, Stehlik J, International Society for H. Lung T. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: sixteenth official pediatric lung and heart-lung transplantation report--2013; focus theme: age. The Journal of heart and lung transplantation : the official publication of the International Society for Heart Transplantation. 2013;32:989–997. - PubMed
-
- Valapour M, Paulson K, Smith JM, Hertz MI, Skeans MA, Heubner BM, Edwards LB, Snyder JJ, Israni AK, Kasiske BL. OPTN/SRTR 2011 Annual Data Report: lung. Am J Transplant. 2013;13(Suppl 1):149–177. - PubMed
-
- Casswell GK, Pilcher DV, Martin RS, Pellegrino VA, Marasco SF, Robertson C, Butt W, Buckland M, Gooi J, Snell GI, Westall GP. Buying time: The use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation as a bridge to lung transplantation in pediatric patients. Pediatric transplantation. 2013;17:E182–188. - PubMed
-
- Strueber M. Bridges to lung transplantation. Current opinion in organ transplantation. 2011;16:458–461. - PubMed
-
- Turner DA, Cheifetz IM, Rehder KJ, Williford WL, Bonadonna D, Banuelos SJ, Peterson-Carmichael S, Lin SS, Davis RD, Zaas D. Active rehabilitation and physical therapy during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation while awaiting lung transplantation: a practical approach. Critical care medicine. 2011;39:2593–2598. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

