Interarticulator coordination in children with and without cerebral palsy
- PMID: 25905558
- PMCID: PMC5529053
- DOI: 10.3109/17518423.2015.1022809
Interarticulator coordination in children with and without cerebral palsy
Abstract
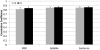
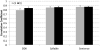
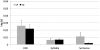
The current study investigates how interarticulator coordination changes across speaking tasks varying in articulatory and linguistic demands for children with CP and their typically-developing peers. Articulatory movements from 12 children with spastic CP (7M, 5F, 4-15 years of age) and 12 typically-developing age- and sex-matched peers were cross-correlated to determine the degree of spatial and temporal coupling between the upper lip and jaw, lower lip and jaw, and upper and lower lips. Spatial and temporal coupling were also correlated with intelligibility. Results indicated that children with CP have reduced spatial coupling between the upper and lower lips and reduced temporal coupling between all articulators as compared to their typically-developing peers. For all participants, sentences were produced with the greatest degree of interarticulator coordination when compared to the diadochokinetic and syllable repetition tasks. Measures of interarticulator coordination were correlated with intelligibility for the speakers with CP.
Keywords: Cerebral palsy; dysarthria; intelligibility; speech motor control.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Articulatory and Vocal Fold Movement Patterns During Loud Speech in Children With Cerebral Palsy.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2024 Feb 12;67(2):477-493. doi: 10.1044/2023_JSLHR-23-00411. Epub 2024 Jan 16. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2024. PMID: 38227476 Free PMC article.
-
Speech-associated labiomandibular movement in Mandarin-speaking children with quadriplegic cerebral palsy: a kinematic study.Res Dev Disabil. 2011 Nov-Dec;32(6):2595-601. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2011.06.016. Epub 2011 Jul 19. Res Dev Disabil. 2011. PMID: 21775100
-
Effects of speech cues in French-speaking children with dysarthria.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2020 May;55(3):401-416. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12526. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2020. PMID: 32077196
-
Intelligibility of 4-year-old children with and without cerebral palsy.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2012 Aug;55(4):1177-89. doi: 10.1044/1092-4388(2011/11-0083). Epub 2012 Jan 9. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2012. PMID: 22232403 Free PMC article.
-
Dysarthria in Mandarin-Speaking Children With Cerebral Palsy: Speech Subsystem Profiles.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2018 Mar 15;61(3):525-548. doi: 10.1044/2017_JSLHR-S-17-0065. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2018. PMID: 29471380 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Articulatory and Vocal Fold Movement Patterns During Loud Speech in Children With Cerebral Palsy.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2024 Feb 12;67(2):477-493. doi: 10.1044/2023_JSLHR-23-00411. Epub 2024 Jan 16. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2024. PMID: 38227476 Free PMC article.
-
Speech Sound Disorders in Children: An Articulatory Phonology Perspective.Front Psychol. 2020 Jan 28;10:2998. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02998. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32047453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A first investigation of tongue, lip, and jaw movements in persons with dysarthria due to multiple sclerosis.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019 Jan;27:188-194. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2018.10.116. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019. PMID: 30399501 Free PMC article.
-
Initial Observations of Lingual Movement Characteristics of Children With Cerebral Palsy.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2017 Jun 22;60(6S):1780-1790. doi: 10.1044/2017_JSLHR-S-16-0239. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2017. PMID: 28655047 Free PMC article.
-
Range and Precision of Formant Movement in Pediatric Dysarthria.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2017 Jul 12;60(7):1864-1876. doi: 10.1044/2017_JSLHR-S-15-0438. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2017. PMID: 28655064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bax M, Goldstein M, Rosenbaum P, Leviton A, Paneth N, Dan B, Jacobsson B, Damiano D. Proposed definition and classification of Cerebral Palsy. April 2005. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology. 2005;47:571–576. - PubMed
-
- Rosenbaum P, Paneth N, Leviton A, Goldstein M, Bax M, Damiano D, Jacobsson B. A report: The definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology. 2007;49:8–14. - PubMed
-
- Sigurdardottir S, Vik T. Speech, expressive language, and verbal cognition of preschool children with cerebral palsy in Iceland: Speech, Language, and Cognition in CP. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology. 2011;53:74–80. - PubMed
-
- Parkes J, Hill N, Platt MJ, Donnelly C. Oromotor dysfunction and communication impairments in children with cerebral palsy: A register study. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology. 2010;52:1113–1119. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
