Selective targeting of the IL23 pathway: Generation and characterization of a novel high-affinity humanized anti-IL23A antibody
- PMID: 25905918
- PMCID: PMC4622456
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2015.1032491
Selective targeting of the IL23 pathway: Generation and characterization of a novel high-affinity humanized anti-IL23A antibody
Abstract
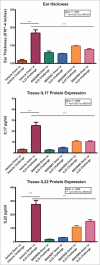
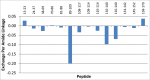
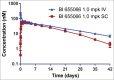
Herein, we describe the generation and characterization of BI 655066, a novel, highly potent neutralizing anti-interleukin-23 (IL23) monoclonal antibody in clinical development for autoimmune conditions, including psoriasis and Crohn's disease. IL23 is a key driver of the differentiation, maintenance, and activity of a number of immune cell subsets, including T helper 17 (Th17) cells, which are believed to mediate the pathogenesis of several immune-mediated disorders. Thus, IL23 neutralization is an attractive therapeutic approach. Designing an antibody for clinical activity and convenience for the patient requires certain properties, such as high affinity, specificity, and solubility. These properties were achieved by directed design of the immunization, lead identification, and humanization procedures. Favorable substance and pharmacokinetic properties were established by biophysical assessments and studies in cynomolgus monkeys.
Keywords: ADCC, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; AUC, analytical ultracentrifugation; BI 655066; CCG, Chemical Computing Group; CDRs, complementarity-determining regions; CH, constant region; Cκ, constant kappa; DMF, dimethylformamide; EOF, electro-osmotic flow; ESI, electrospray ionization; F, phenylalanine; G, glycine; GAHA, goat anti-human IgG gamma antibody; HCLF, high concentration liquid formulation; IL12, Interleukin 12; IL12RB1, IL12 receptor subunit beta 1; IL23, Interleukin-23; IL23R, IL23 receptor; JAK2, Janus kinase 2; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; PK, pharmacokinetic; RU, resonance units; SEC, size-exclusion chromatography; SPR, surface plasmon resonance; Th17, T helper 17 cells; UV, ultraviolet; V, variable; VH, variable heavy; Vκ, variable kappa; Y, tyrosine; biophysical assessment; humanization; immunogen design; pharmacokinetic profile; tyk2, tyrosine kinase 2.
Figures



References
-
- Baeten DL, Kuchroo VK. How Cytokine networks fuel inflammation: interleukin-17 and a tale of two autoimmune diseases. Nat Med 2013; 19:824-5; PMID:23836225; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nm.3268 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gaffen SL, Jain R, Garg AV, Cua DJ. The IL-23-IL-17 immune axis: from mechanisms to therapeutic testing. Nat Rev Immunol 2014; 14:585-600; PMID:25145755; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nri3707 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Toussirot E. The IL23/Th17 pathway as a therapeutic target in chronic inflammatory diseases. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 2012; 11:159-68; PMID:22280236; http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/187152812800392805 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Elmaagacli AH, Koldehoff M, Landt O, Beelen DW. Relation of an interleukin-23 receptor gene polymorphism to graft-versus-host disease after hematopoietic-cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2008; 41:821-6; PMID:18209723; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705980 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Capon F, Di MP, Szaub J, Prescott NJ, Dunster C, Baumber L, Timms K, Gutin A, Abkevic V, Burden AD, et al.. Sequence variants in the genes for the interleukin-23 receptor (IL23R) and its ligand (IL12B) confer protection against psoriasis. Hum Genet 2007; 122:201-6; PMID:17587057; http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00439-007-0397-0 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
