Expression Profiles and Clinical Significance of MicroRNAs in Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma: A STROBE-Compliant Observational Study
- PMID: 25906110
- PMCID: PMC4602701
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000767
Expression Profiles and Clinical Significance of MicroRNAs in Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma: A STROBE-Compliant Observational Study
Abstract
Papillary renal cell carcinoma (pRCC) is the second most prevalent subtype of kidney cancers. In the current study, we analyzed the global microRNA (miRNA) expression profiles in pRCC, with the aim to evaluate the relationship of miRNA expression with the progression and prognosis of pRCC.A total of 163 treatment-naïve primary pRCC patients were identified from the Cancer Genome Atlas dataset and included in this retrospective observational study. The miRNA expression profiles were graded by tumor-node-metastasis information, and compared between histologic subtypes. Furthermore, the training-validation approach was applied to identify miRNAs of prognostic values, with the aid of Kaplan-Meier survival, and univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses. Finally, the online DAVID (Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discover) program was applied for the pathway enrichment analysis with the target genes of prognosis-associated miRNAs, which were predicted by 3 computational algorithms (PicTar, TargetScan, and Miranda).In the progression-related miRNA profiles, 26 miRNAs were selected for pathologic stage, 28 for pathologic T, 16 for lymph node status, 3 for metastasis status, and 32 for histologic types, respectively. In the training stage, the expression levels of 12 miRNAs (mir-134, mir-379, mir-127, mir-452, mir-199a, mir-200c, mir-141, mir-3074, mir-1468, mir-181c, mir-1180, and mir-34a) were significantly associated with patient survival, whereas mir-200c, mir-127, mir-34a, and mir-181c were identified by multivariate Cox regression analyses as potential independent prognostic factors in pRCC. Subsequently, mir-200c, mir-127, and mir-34a were confirmed to be significantly correlated with patient survival in the validation stage. Finally, target gene prediction analysis identified a total of 113 target genes for mir-200c, 37 for mir-127, and 180 for mir-34a, which further generated 15 molecular pathways.Our results identified the specific miRNAs associated with the progression and aggressiveness of pRCC, and 3 miRNAs (mir-200c, mir-127, and mir-34a) as promising prognostic factors of pRCC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


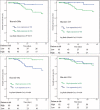
References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, et al. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA: Cancer J Clin 2014; 64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Rini BI, Campbell SC, Escudier B. Renal cell carcinoma. Lancet 2009; 373:1119–1132. - PubMed
-
- Cronin RE, Kaehny WD, Miller PD, et al. Renal cell carcinoma: unusual systemic manifestations. Medicine 1976; 55:291–311. - PubMed
-
- Twardowski PW, Mack PC, Lara PN., Jr Papillary renal cell carcinoma: current progress and future directions. Clin Genitourinary Cancer 2014; 12:74–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

