Micromilling: a method for ultra-rapid prototyping of plastic microfluidic devices
- PMID: 25906246
- PMCID: PMC4439323
- DOI: 10.1039/c5lc00234f
Micromilling: a method for ultra-rapid prototyping of plastic microfluidic devices
Abstract
This tutorial review offers protocols, tips, insight, and considerations for practitioners interested in using micromilling to create microfluidic devices. The objective is to provide a potential user with information to guide them on whether micromilling would fill a specific need within their overall fabrication strategy. Comparisons are made between micromilling and other common fabrication methods for plastics in terms of technical capabilities and cost. The main discussion focuses on "how-to" aspects of micromilling, to enable a user to select proper equipment and tools, and obtain usable microfluidic parts with minimal start-up time and effort. The supplementary information provides more extensive discussion on CNC mill setup, alignment, and programming. We aim to reach an audience with minimal prior experience in milling, but with strong interests in fabrication of microfluidic devices.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: D.J.G and D.J.B. hold equity in Salus Discovery, LLC and Tasso, Inc.
Figures
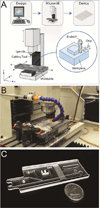


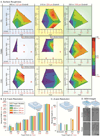
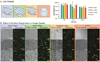
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

