Melatonin modulates the fetal cardiovascular defense response to acute hypoxia
- PMID: 25908097
- PMCID: PMC4528231
- DOI: 10.1111/jpi.12242
Melatonin modulates the fetal cardiovascular defense response to acute hypoxia
Abstract
Experimental studies in animal models supporting protective effects on the fetus of melatonin in adverse pregnancy have prompted clinical trials in human pregnancy complicated by fetal growth restriction. However, the effects of melatonin on the fetal defense to acute hypoxia, such as that which may occur during labor, remain unknown. This translational study tested the hypothesis, in vivo, that melatonin modulates the fetal cardiometabolic defense responses to acute hypoxia in chronically instrumented late gestation fetal sheep via alterations in fetal nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability. Under anesthesia, 6 fetal sheep at 0.85 gestation were instrumented with vascular catheters and a Transonic flow probe around a femoral artery. Five days later, fetuses were exposed to acute hypoxia with or without melatonin treatment. Fetal blood was taken to determine blood gas and metabolic status and plasma catecholamine concentrations. Hypoxia during melatonin treatment was repeated during in vivo NO blockade with the NO clamp. This technique permits blockade of de novo synthesis of NO while compensating for the tonic production of the gas, thereby maintaining basal cardiovascular function. Melatonin suppressed the redistribution of blood flow away from peripheral circulations and the glycemic and plasma catecholamine responses to acute hypoxia. These are important components of the fetal brain sparing response to acute hypoxia. The effects of melatonin involved NO-dependent mechanisms as the responses were reverted by fetal treatment with the NO clamp. Melatonin modulates the in vivo fetal cardiometabolic responses to acute hypoxia by increasing NO bioavailability.
Keywords: cardiovascular; hypoxia; melatonin; nitric oxide; oxidative stress.
© 2015 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

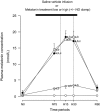
 ; n = 6), treatment with melatonin high (0.5 ± 0.1 μg/kg/min; •; n = 6), or treatment with melatonin high during nitric oxide (NO) blockade with the NO clamp (□; n = 6). Significant differences: aP < 0.05, versus time period N0; bP < 0.05, versus saline vehicle infusion; cP < 0.05, melatonin low versus melatonin high (two-way RM ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test).
; n = 6), treatment with melatonin high (0.5 ± 0.1 μg/kg/min; •; n = 6), or treatment with melatonin high during nitric oxide (NO) blockade with the NO clamp (□; n = 6). Significant differences: aP < 0.05, versus time period N0; bP < 0.05, versus saline vehicle infusion; cP < 0.05, melatonin low versus melatonin high (two-way RM ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test).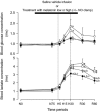
 ; n = 6), treatment with melatonin high (0.5 ± 0.1 μg/kg/min; •; n = 6), or treatment with melatonin high during nitric oxide (NO) blockade with the NO clamp (□; n = 6). Significant differences: aP < 0.05, versus time period N0; bP < 0.05, versus saline vehicle infusion; cP < 0.05, melatonin low versus melatonin high (two-way RM ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test).
; n = 6), treatment with melatonin high (0.5 ± 0.1 μg/kg/min; •; n = 6), or treatment with melatonin high during nitric oxide (NO) blockade with the NO clamp (□; n = 6). Significant differences: aP < 0.05, versus time period N0; bP < 0.05, versus saline vehicle infusion; cP < 0.05, melatonin low versus melatonin high (two-way RM ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test).
 ; n = 6), treatment with melatonin high (0.5 ± 0.1 μg/kg/min; •; n = 6), or treatment with melatonin high during nitric oxide (NO) blockade with the NO clamp (□; n = 6). Significant differences: aP < 0.05, versus time period N1; bP < 0.05, versus saline vehicle infusion; cP < 0.05, melatonin low versus melatonin high (two-way RM ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test).
; n = 6), treatment with melatonin high (0.5 ± 0.1 μg/kg/min; •; n = 6), or treatment with melatonin high during nitric oxide (NO) blockade with the NO clamp (□; n = 6). Significant differences: aP < 0.05, versus time period N1; bP < 0.05, versus saline vehicle infusion; cP < 0.05, melatonin low versus melatonin high (two-way RM ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test).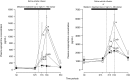
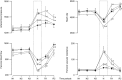
 ; n = 6), treatment with melatonin high (0.5 ± 0.1 μg/kg/min; •; n = 6), or treatment with melatonin high during nitric oxide (NO) blockade with the NO clamp (□; n = 6). Significant differences: aP < 0.05, versus time period N0; bP < 0.05, versus saline vehicle infusion; cP < 0.05, melatonin low versus melatonin high (two-way RM ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test).
; n = 6), treatment with melatonin high (0.5 ± 0.1 μg/kg/min; •; n = 6), or treatment with melatonin high during nitric oxide (NO) blockade with the NO clamp (□; n = 6). Significant differences: aP < 0.05, versus time period N0; bP < 0.05, versus saline vehicle infusion; cP < 0.05, melatonin low versus melatonin high (two-way RM ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test).Similar articles
-
Statin treatment depresses the fetal defence to acute hypoxia via increasing nitric oxide bioavailability.J Physiol. 2012 Jan 15;590(2):323-34. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.217968. Epub 2011 Nov 21. J Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22106179 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced nitric oxide activity offsets peripheral vasoconstriction during acute hypoxaemia via chemoreflex and adrenomedullary actions in the sheep fetus.J Physiol. 2003 Feb 15;547(Pt 1):283-91. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.032615. Epub 2003 Jan 10. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12562956 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin and vitamin C increase umbilical blood flow via nitric oxide-dependent mechanisms.J Pineal Res. 2010 Nov;49(4):399-406. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2010.00813.x. Epub 2010 Sep 24. J Pineal Res. 2010. PMID: 20958954
-
PHYSIOLOGY AND ENDOCRINOLOGY SYMPOSIUM: Alterations in uteroplacental hemodynamics during melatonin supplementation in sheep and cattle.J Anim Sci. 2017 May;95(5):2211-2221. doi: 10.2527/jas.2016.1151. J Anim Sci. 2017. PMID: 28726984 Review.
-
The fetal brain sparing response to hypoxia: physiological mechanisms.J Physiol. 2016 Mar 1;594(5):1215-30. doi: 10.1113/JP271099. Epub 2016 Jan 6. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26496004 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acute hypoxia-reoxygenation and vascular oxygen sensing in the chicken embryo.Physiol Rep. 2017 Nov;5(22):e13501. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13501. Physiol Rep. 2017. PMID: 29146864 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular function in term fetal sheep conceived, gestated and studied in the hypobaric hypoxia of the Andean altiplano.J Physiol. 2016 Mar 1;594(5):1231-45. doi: 10.1113/JP271110. Epub 2015 Oct 1. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26339865 Free PMC article.
-
Disturbances in Maternal Steroidogenesis and Appearance of Intrauterine Growth Retardation at High-Altitude Environments Are Established from Early Pregnancy. Effects of Treatment with Antioxidant Vitamins.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 11;10(11):e0140902. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140902. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26560325 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal Hypoxia Affects Foetal Cardiovascular Regulatory Mechanisms in a Sex- and Circadian-Dependent Manner: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 7;23(5):2885. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052885. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35270026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Supplementary Tryptophan Fed to Sows Prior to and after Farrowing to Improve Piglet Growth and Survival.Animals (Basel). 2021 Aug 30;11(9):2540. doi: 10.3390/ani11092540. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reiter RJ, Tamura H, Tan DX, et al. Melatonin and the circadian system: contributions to successful female reproduction. Fertil Steril. 2014;102:321–328. - PubMed
-
- Kivela A. Serum melatonin during human pregnancy. Acta Endocrinol. 1991;124:233–237. - PubMed
-
- Lee CK, Moon DH, Shin CS, et al. Circadian expression of Mel1a and PL-II genes in placenta: effects of melatonin on the PL-II gene expression in the rat placenta. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2003;200:57–66. - PubMed
-
- Bonnefont-Rousselot D, Collin F. Melatonin: action as antioxidant and potential applications in human disease and aging. Toxicology. 2010;278:55–67. - PubMed
-
- Galano A, Tan DX, Reiter RJ. On the free radical scavenging activities of melatonin's metabolites, AFMK and AMK. J Pineal Res. 2013;54:245–257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

