Asthma predicts cardiovascular disease events: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis
- PMID: 25908767
- PMCID: PMC4441553
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.305452
Asthma predicts cardiovascular disease events: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis
Abstract
Objectives: To identify and characterize an association between persistent asthma and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA).
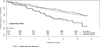
Approach and results: MESA is a longitudinal prospective study of an ethnically diverse cohort of individuals free of known CVD at its inception. The presence and severity of asthma were assessed in the MESA at examination 1. Persistent asthma was defined as asthmatics using controller medications (inhaled corticosteroids, leukotriene inhibitors, and oral corticosteroids) and intermittent asthma as asthmatics not using controller medications. Participants were followed up for a mean (SD) of 9.1 (2.8) years for development of incident CVD (coronary death, myocardial infarction, angina, stroke, and CVD death). Multivariable Cox regression models were used to assess associations of asthma and CVD. The 6792 participants were 62.2 (SD, 10.2) years old: 47% men (28% black, 22% Hispanic, and 12% Chinese). Persistent asthmatics (n=156), compared with intermittent (n=511) and nonasthmatics (n=6125), respectively, had higher C-reactive protein (1.2 [1.2] versus 0.9 [1.2] versus 0.6 [1.2] mg/L) and fibrinogen (379 [88] versus 356 [80] versus 345 [73] mg/dL) levels. Persistent asthmatics had the lowest unadjusted CVD-free survival rate of 84.1%, 95% confidence interval (78.9%-90.3%) compared with intermittent asthmatics 91.1% (88.5%-93.8%) and nonasthmatics 90.2% (89.4%-91%). Persistent asthmatics had greater risk of CVD events than nonasthmatics (hazard ratio [95% confidence interval], 1.6 [1.01-2.5]; P=0.040]), even after adjustment for age, sex, race, CVD risk factors, and antihypertensive and lipid medication use.
Conclusions: In this large multiethnic cohort, persistent asthmatics had a higher CVD event rate than nonasthmatics.
Keywords: asthma; atherosclerosis; epidemiology; risk factors.
© 2015 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Akinbami LJ, Moorman JE, Bailey C, Zahran HS, King M, Johnson CA, Liu X. Trends in asthma prevalence, health care use, and mortality in the United States, 2001–2010. NCHS Data Brief. 2012:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Hansson GK. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1685–1695. - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Hennekens CH, Buring JE, Rifai N. C-reactive protein and other markers of inflammation in the prediction of cardiovascular disease in women. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:836–843. - PubMed
-
- Solomon DH, Karlson EW, Rimm EB, Cannuscio CC, Mandl LA, Manson JE, Stampfer MJ, Curhan GC. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in women diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis. Circulation. 2003;107:1303–1307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-TR-000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007936/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL077612/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR001874/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-TR-001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL07936/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials