Targeting chromatin binding regulation of constitutively active AR variants to overcome prostate cancer resistance to endocrine-based therapies
- PMID: 25908785
- PMCID: PMC4499120
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv262
Targeting chromatin binding regulation of constitutively active AR variants to overcome prostate cancer resistance to endocrine-based therapies
Abstract
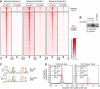
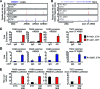
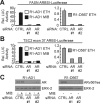
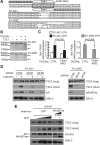
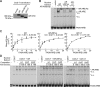
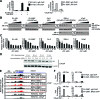
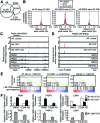
Androgen receptor (AR) variants (AR-Vs) expressed in prostate cancer (PCa) lack the AR ligand binding domain (LBD) and function as constitutively active transcription factors. AR-V expression in patient tissues or circulating tumor cells is associated with resistance to AR-targeting endocrine therapies and poor outcomes. Here, we investigated the mechanisms governing chromatin binding of AR-Vs with the goal of identifying therapeutic vulnerabilities. By chromatin immunoprecipitation and sequencing (ChIP-seq) and complementary biochemical experiments, we show that AR-Vs display a binding preference for the same canonical high-affinity androgen response elements (AREs) that are preferentially engaged by AR, albeit with lower affinity. Dimerization was an absolute requirement for constitutive AR-V DNA binding and transcriptional activation. Treatment with the bromodomain and extraterminal (BET) inhibitor JQ1 resulted in inhibition of AR-V chromatin binding and impaired AR-V driven PCa cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Importantly, this was associated with a novel JQ1 action of down-regulating AR-V transcript and protein expression. Overall, this study demonstrates that AR-Vs broadly restore AR chromatin binding events that are otherwise suppressed during endocrine therapy, and provides pre-clinical rationale for BET inhibition as a strategy for inhibiting expression and chromatin binding of AR-Vs in PCa.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



References
-
- Matusik R.J., Jin R.J., Sun Q., Wang Y., Yu X., Gupta A., Nandana S., Case T.C., Paul M., Mirosevich J., et al. Prostate epithelial cell fate. Differentiation. 2008;76:682–698. - PubMed
-
- Ryan C.J., Tindall D.J. Androgen receptor rediscovered: the new biology and targeting the androgen receptor therapeutically. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011;29:3651–3658. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

