Methionine increases BDNF DNA methylation and improves memory in epilepsy
- PMID: 25909085
- PMCID: PMC4402085
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.183
Methionine increases BDNF DNA methylation and improves memory in epilepsy
Abstract
Objective: Temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) patients exhibit signs of memory impairments even when seizures are pharmacologically controlled. Surprisingly, the underlying molecular mechanisms involved in TLE-associated memory impairments remain elusive. Memory consolidation requires epigenetic transcriptional regulation of genes in the hippocampus; therefore, we aimed to determine how epigenetic DNA methylation mechanisms affect learning-induced transcription of memory-permissive genes in the epileptic hippocampus.
Methods: Using the kainate rodent model of TLE and focusing on the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (Bdnf) gene as a candidate of DNA methylation-mediated transcription, we analyzed DNA methylation levels in epileptic rats following learning. After detection of aberrant DNA methylation at the Bdnf gene, we investigated functional effects of altered DNA methylation on hippocampus-dependent memory formation in our TLE rodent model.
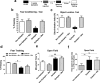
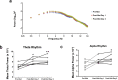
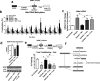
Results: We found that behaviorally driven BdnfDNA methylation was associated with hippocampus-dependent memory deficits. Bisulfite sequencing revealed that decreased BdnfDNA methylation levels strongly correlated with abnormally high levels of BdnfmRNA in the epileptic hippocampus during memory consolidation. Methyl supplementation via methionine (Met) increased BdnfDNA methylation and reduced BdnfmRNA levels in the epileptic hippocampus during memory consolidation. Met administration reduced interictal spike activity, increased theta rhythm power, and reversed memory deficits in epileptic animals. The rescue effect of Met treatment on learning-induced BdnfDNA methylation, Bdnf gene expression, and hippocampus-dependent memory, were attenuated by DNA methyltransferase blockade.
Interpretation: Our findings suggest that manipulation of DNA methylation in the epileptic hippocampus should be considered as a viable treatment option to ameliorate memory impairments associated with TLE.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Status epilepticus triggers early and late alterations in brain-derived neurotrophic factor and NMDA glutamate receptor Grin2b DNA methylation levels in the hippocampus.Neuroscience. 2013 Sep 17;248:602-19. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.06.029. Epub 2013 Jun 27. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23811393 Free PMC article.
-
Interictal serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor level reflects white matter integrity, epilepsy severity, and cognitive dysfunction in chronic temporal lobe epilepsy.Epilepsy Behav. 2016 Jun;59:147-54. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2016.02.029. Epub 2016 May 3. Epilepsy Behav. 2016. PMID: 27152461
-
The cognitive impairment induced by zinc deficiency in rats aged 0∼2 months related to BDNF DNA methylation changes in the hippocampus.Nutr Neurosci. 2017 Nov;20(9):519-525. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2016.1194554. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Nutr Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 27329329
-
To BDNF or not to BDNF: that is the epileptic hippocampus.Neuroscientist. 2005 Aug;11(4):282-7. doi: 10.1177/1073858405278266. Neuroscientist. 2005. PMID: 16061515 Review.
-
Long-term memory deficits in temporal lobe epilepsy.Rev Neurol (Paris). 2017 Jul-Aug;173(7-8):490-497. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2017.06.011. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2017. PMID: 28838789 Review.
Cited by
-
Interplay between Metabolism, Nutrition and Epigenetics in Shaping Brain DNA Methylation, Neural Function and Behavior.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jul 3;11(7):742. doi: 10.3390/genes11070742. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32635190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Etiology matters - Genomic DNA Methylation Patterns in Three Rat Models of Acquired Epilepsy.Sci Rep. 2016 May 9;6:25668. doi: 10.1038/srep25668. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27157830 Free PMC article.
-
Methotrexate Neurotoxicity Is Related to Epigenetic Modification of the Myelination Process.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 23;22(13):6718. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136718. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34201550 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic mechanisms of neurodegenerative diseases and acute brain injury.Neurochem Int. 2020 Feb;133:104642. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2019.104642. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Neurochem Int. 2020. PMID: 31838024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prelimbic Cortical Stimulation with L-methionine Enhances Cognition through Hippocampal DNA Methylation and Neuroplasticity Mechanisms.Aging Dis. 2023 Feb 1;14(1):112-135. doi: 10.14336/AD.2022.0706. eCollection 2023 Feb 1. Aging Dis. 2023. PMID: 36818556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kleen JK, Scott RC, Lenck-Santini PP, Holmes GL. Cognitive and behavioral co-morbidities of epilepsy. In: Noebels JL, Avoli M, Rogawski MA, Olsen RW, Delgado-Escueta AV, editors. Jasper's basic mechanisms of the epilepsies. 4th ed. Bethesda, MD: Oxford University Press; 2012. pp. 915–929.
-
- Levenson JM, Roth TL, Lubin FD, et al. Evidence that DNA (cytosine-5) methyltransferase regulates synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:15763–15773. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

