Structural Analysis of the 14-3-3ζ/Chibby Interaction Involved in Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling
- PMID: 25909186
- PMCID: PMC4409382
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123934
Structural Analysis of the 14-3-3ζ/Chibby Interaction Involved in Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling
Abstract
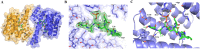
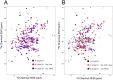
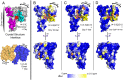
The partially disordered Chibby (Cby) is a conserved nuclear protein that antagonizes the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. By competing with the Tcf/Lef family proteins for binding to β-catenin, Cby abrogates the β-catenin-mediated transcription of Wnt signaling genes. Additionally, upon phosphorylation on S20 by the kinase Akt, Cby forms a complex with 14-3-3 to facilitate the nuclear export of β-catenin, which represents another crucial mechanism for the regulation of Wnt signaling. To obtain a mechanistic understanding of the 14-3-3/Cby interaction, we have extensively characterized the complex using X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC). The crystal structure of the human 14-3-3ζ/Cby protein-peptide complex reveals a canonical binding mode; however the residue at the +2 position from the phosphorylated serine is shown to be uniquely oriented relative to other solved structures of 14-3-3 complexes. Our ITC results illustrate that although the phosphorylation of S20 is essential for Cby to recognize 14-3-3, residues flanking the phosphorylation site also contribute to the binding affinity. However, as is commonly observed in other 14-3-3/phosphopeptide crystal structures, residues of Cby flanking the 14-3-3 binding motif lack observable electron density. To obtain a more detailed binding interface, we have completed the backbone NMR resonance assignment of 14-3-3ζ. NMR titration experiments reveal that residues outside of the 14-3-3 conserved binding cleft, namely a flexible loop consisting of residues 203-210, are also involved in binding Cby. By using a combined X-ray and NMR approach, we have dissected the molecular basis of the 14-3-3/Cby interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Takemaru K, Yamaguchi S, Lee YS, Zhang Y, Carthew RW, Moon RT (2003) Chibby, a nuclear beta-catenin-associated antagonist of the Wnt/Wingless pathway. Nature 422: 905–909. - PubMed
-
- Clevers H (2006) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell 127: 469–480. - PubMed
-
- Logan CY, Nusse R (2004) The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 20: 781–810. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

