MicroRNA-21 plays an oncogenic role by targeting FOXO1 and activating the PI3K/AKT pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 25909227
- PMCID: PMC4558134
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3729
MicroRNA-21 plays an oncogenic role by targeting FOXO1 and activating the PI3K/AKT pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
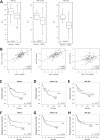
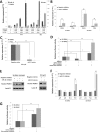
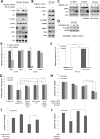
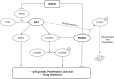
The prognostic implications of miR-21, miR-17-92 and miR-155 were evaluated in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients, and novel mechanism by which miR-21 contributes to the oncogenesis of DLBCL by regulating FOXO1 and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway was investigated. The expressions of miR-21, miR-17-92 and miR-155 measured by quantitative reverse-transcription-PCR were significantly up-regulated in DLBCL tissues (n=200) compared to control tonsils (P=0.012, P=0.001 and P<0.0001). Overexpression of miR-21 and miR-17-92 was significantly associated with shorter progression-free survival (P=0.003 and P=0.014) and overall survival (P=0.004 and P=0.012). High miR-21 was an independent prognostic factor in DLBCL patients treated with rituximab-combined chemotherapy. MiR-21 level was inversely correlated with the levels of FOXO1 and PTEN in DLBCL cell lines. Reporter-gene assay showed that miR-21 directly targeted and suppressed the FOXO1 expression, and subsequently inhibited Bim transcription in DLBCL cells. MiR-21 also down-regulated PTEN expression and consequently activated the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, which further decreased FOXO1 expression. Moreover, miR-21 inhibitor suppressed the expression and activity of MDR1, thereby sensitizing DLBCL cells to doxorubicin. These data demonstrated that miR-21 plays an important oncogenic role in DLBCL by modulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/FOXO1 pathway at multiple levels resulting in strong prognostic implication. Therefore, targeting miR-21 may have therapeutic relevance in DLBCL.
Keywords: FOXO1; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; miR-155; miR-17-92 cluster; miR-21.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Lossos IS, Morgensztern D. Prognostic biomarkers in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:995–1007. - PubMed
-
- Monti S, Savage KJ, Kutok JL, Feuerhake F, Kurtin P, Mihm M, Wu B, Pasqualucci L, Neuberg D, Aguiar RC, Dal Cin P, Ladd C, Pinkus GS, Salles G, Harris NL, Dalla-Favera R, et al. Molecular profiling of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies robust subtypes including one characterized by host inflammatory response. Blood. 2005;105:1851–1861. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

