Structural features of a 3' splice site in influenza a
- PMID: 25909229
- PMCID: PMC4455060
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00012
Structural features of a 3' splice site in influenza a
Abstract
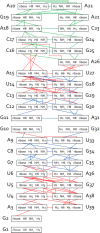
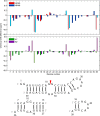
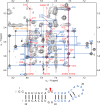
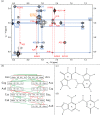
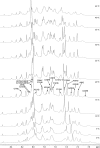
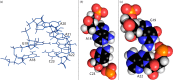
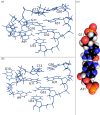
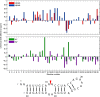
Influenza A is an RNA virus with a genome of eight negative sense segments. Segment 7 mRNA contains a 3' splice site for alternative splicing to encode the essential M2 protein. On the basis of sequence alignment and chemical mapping experiments, the secondary structure surrounding the 3' splice site has an internal loop, adenine bulge, and hairpin loop when it is in the hairpin conformation that exposes the 3' splice site. We report structural features of a three-dimensional model of the hairpin derived from nuclear magnetic resonance spectra and simulated annealing with restrained molecular dynamics. Additional insight was provided by modeling based on (1)H chemical shifts. The internal loop containing the 3' splice site has a dynamic guanosine and a stable imino (cis Watson-Crick/Watson-Crick) GA pair. The adenine bulge also appears to be dynamic with the A either stacked in the stem or forming a base triple with a Watson-Crick GC pair. The hairpin loop is a GAAA tetraloop closed by an AC pair.
Figures




References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2010) Estimates of deaths associated with seasonal influenza: United States, 1976–2007. In Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, pp 1057–1062, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta. - PubMed
-
- Thompson W. W.; Shay D. K.; Weintraub E.; Brammer L.; Bridges C. B.; Cox N. J.; Fukuda K. F. (2004) Influenza-associated hospitalizations in the United States. JAMA, J. Am. Med. Assoc. 292, 1333–1340. - PubMed
-
- Baigent S. J.; McCauley J. W. (2003) Influenza type A in humans, mammals and birds: Determinants of virus virulence, host-range and interspecies transmission. BioEssays 25, 657–671. - PubMed
-
- Hsu J.; Santesso N.; Mustafa R.; Brozek J.; Chen Y. L.; Hopkins J. P.; Cheung A.; Hovhannisyan G.; Ivanova L.; Flottorp S. A.; Sæterdal I.; Wong A. D.; Tian J.; Uyeki T. M.; Akl E. A.; Alonso-Coello P.; Smaill F.; Schünemann H. J. (2012) Antivirals for treatment of influenza: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Ann. Int. Med. 156, 512–524. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dharan N. J.; Gubareva L. V.; Meyer J. J.; Okomo-Adhiambo M.; McClinton R. C.; Marshall S. A.; St. George K.; Epperson S.; Brammer L.; Klimov A. I.; Bresee J. S.; Fry A. M. (2009) Infections with oseltamivir-resistant influenza A(H1N1) virus in the United States. JAMA, J. Am. Med. Assoc. 301, 1034–1041. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

