Loss of the N-terminal methyltransferase NRMT1 increases sensitivity to DNA damage and promotes mammary oncogenesis
- PMID: 25909287
- PMCID: PMC4494936
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3653
Loss of the N-terminal methyltransferase NRMT1 increases sensitivity to DNA damage and promotes mammary oncogenesis
Abstract
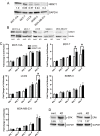
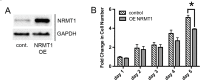
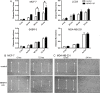
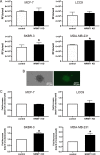
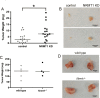
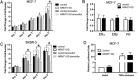
Though discovered over four decades ago, the function of N-terminal methylation has mostly remained a mystery. Our discovery of the first mammalian N-terminal methyltransferase, NRMT1, has led to the discovery of many new functions for N-terminal methylation, including regulation of DNA/protein interactions, accurate mitotic division, and nucleotide excision repair (NER). Here we test whether NRMT1 is also important for DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair, and given its previously known roles in cell cycle regulation and the DNA damage response, assay if NRMT1 is acting as a tumor suppressor. We find that NRMT1 knockdown significantly enhances the sensitivity of breast cancer cell lines to both etoposide treatment and γ-irradiation, as well as, increases proliferation rate, invasive potential, anchorage-independent growth, xenograft tumor size, and tamoxifen sensitivity. Interestingly, this positions NRMT1 as a tumor suppressor protein involved in multiple DNA repair pathways, and indicates, similar to BRCA1 and BRCA2, its loss may result in tumors with enhanced sensitivity to diverse DNA damaging chemotherapeutics.
Keywords: DNA damage; DNA repair; N-terminal methylation; NRMT1; breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Brosius J, Chen R. The primary structure of protein L16 located at the peptidyltransferase center of Escherichia coli ribosomes. FEBS letters. 1976;68:105–109. - PubMed
-
- Wittmann-Liebold B, Pannenbecker R. Primary structure of protein L33 from the large subunit of the Escherichia coli ribosome. FEBS letters. 1976;68:115–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

