Efficacy of Leukadherin-1 in the Prevention of Hyperoxia-Induced Lung Injury in Neonatal Rats
- PMID: 25909334
- PMCID: PMC4742935
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2014-0422OC
Efficacy of Leukadherin-1 in the Prevention of Hyperoxia-Induced Lung Injury in Neonatal Rats
Abstract
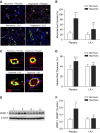
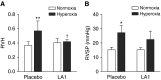
Lung inflammation plays a key role in the pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), a chronic lung disease of premature infants. The challenge in BPD management is the lack of effective and safe antiinflammatory agents. Leukadherin-1 (LA1) is a novel agonist of the leukocyte surface integrin CD11b/CD18 that enhances leukocyte adhesion to ligands and vascular endothelium and thus reduces leukocyte transendothelial migration and influx to the injury sites. Its functional significance in preventing hyperoxia-induced neonatal lung injury is unknown. We tested the hypothesis that administration of LA1 is beneficial in preventing hyperoxia-induced neonatal lung injury, an experimental model of BPD. Newborn rats were exposed to normoxia (21% O2) or hyperoxia (85% O2) and received twice-daily intraperitoneal injection of LA1 or placebo for 14 days. Hyperoxia exposure in the presence of the placebo resulted in a drastic increase in the influx of neutrophils and macrophages into the alveolar airspaces. This increased leukocyte influx was accompanied by decreased alveolarization and angiogenesis and increased pulmonary vascular remodeling and pulmonary hypertension (PH), the pathological hallmarks of BPD. However, administration of LA1 decreased macrophage infiltration in the lungs during hyperoxia. Furthermore, treatment with LA1 improved alveolarization and angiogenesis and decreased pulmonary vascular remodeling and PH. These data indicate that leukocyte recruitment plays an important role in the experimental model of BPD induced by hyperoxia. Targeting leukocyte trafficking using LA1, an integrin agonist, is beneficial in preventing lung inflammation and protecting alveolar and vascular structures during hyperoxia. Thus, targeting integrin-mediated leukocyte recruitment and inflammation may provide a novel strategy in preventing and treating BPD in preterm infants.
Keywords: BPD; LA1; hyperoxia; inflammation; integrin.
Figures



References
-
- Jobe AH, Bancalari E. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:1723–1729. - PubMed
-
- Bhandari A, Bhandari V. Pitfalls, problems, and progress in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics. 2009;123:1562–1573. - PubMed
-
- Stenmark KR, Abman SH. Lung vascular development: implications for pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Annu Rev Physiol. 2005;67:623–661. - PubMed
-
- Speer CP. Inflammation and bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a continuing story. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2006;11:354–362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

