Increasing aminoterminal-pro-B-type natriuretic peptide precedes the development of arterial hypertension: the multiethnic study of atherosclerosis
- PMID: 25909698
- PMCID: PMC4410427
- DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000500
Increasing aminoterminal-pro-B-type natriuretic peptide precedes the development of arterial hypertension: the multiethnic study of atherosclerosis
Abstract
Background: Longitudinal associations between the aminoterminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and incident hypertension are lacking.
Methods: We tested associations between baseline NT-proBNP (bNT-proBNP) and change in NT-proBNP (ΔNT-proBNP) (visit 3 NT-proBNP - bNT-proBNP, 3.2 years apart) with incident hypertension (SBP ≥ 140 and/or DBP ≥90 mmHg or taking antihypertensive medications). Incident hypertension was evaluated in 5596 individuals in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis without hypertension at baseline (53% women, age range 45-84 years without overt cardiovascular disease) and follow-up for 9.5 years and in a subgroup (1550) who had bNT-proBNP less than 100 pg/ml and no hypertension at visit 3. Incident hypertension was regressed (proportional hazards) on quintiles of bNT-proBNP (range) (reference <19.2, 19.3-40.8, 40.9-70.9, 71-135.2, and >135.5) and also on ΔNT-proBNP categories (reference <-10, -10 to 10, >10 to 50, and >50 pg/ml). Hazard ratios were adjusted for age, race, sex, education, diabetes, obesity, left ventricle mass/height, SBP and DBP, interleukin-6, salt intake, estimated glomerular filtration rate, and exercise.
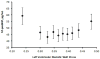
Results: Compared with the reference category, hazard ratios (95% confidence interval) for incident hypertension compared with the first quintile of bNT-proBNP were 1.47 (1.13-1.93), 1.57 (1.18-2.09), 1.52 (1.12-2.06), and 2.36 (1.62-3.41). Hazard ratios for incident hypertension by categories of ΔNT-proBNP from 3.2 to 9.5 years follow-up were 0.98 (0.62-1.56), 1.13 (0.72-1.79), and 1.82 (1.07-3.12).
Conclusion: The development of hypertension tended to be preceded by elevated levels of bNT-proBNP or a substantial positive ΔNT-proBNP.
Figures


Comment in
-
NT-proBNP and the risk of incident hypertension: is change over time a better predictor than baseline value?J Hypertens. 2015 May;33(5):924-5. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000571. J Hypertens. 2015. PMID: 25909693 No abstract available.
References
-
- Buckley MG, Markandu ND, Miller MA, Sagnella GA, MacGregor GA. Plasma concentrations and comparisons of brain and atrial natriuretic peptide in normal subjects and in patients with essential hypertension. Journal of Human Hypertension. 1993;7 (3):245–250. - PubMed
-
- Kohno M, Horio T, Yokokawa K, Murakawa K, Yasunari K, Akioka K, et al. Brain natriuretic peptide as a cardiac hormone in essential hypertension. Am J Med. 1992;92 (1):29–34. - PubMed
-
- Freitag MH, Larson MG, Levy D, Benjamin EJ, Wang TJ, Leip EP, et al. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide levels and blood pressure tracking in the Framingham Heart Study. Hypertension. 2003;41 (4):978–983. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL066075/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC 9808/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL 66075/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC 95168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

