Function of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa NrdR Transcription Factor: Global Transcriptomic Analysis and Its Role on Ribonucleotide Reductase Gene Expression
- PMID: 25909779
- PMCID: PMC4409342
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123571
Function of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa NrdR Transcription Factor: Global Transcriptomic Analysis and Its Role on Ribonucleotide Reductase Gene Expression
Abstract
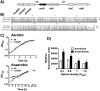
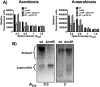
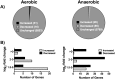
Ribonucleotide reductases (RNRs) are a family of sophisticated enzymes responsible for the synthesis of the deoxyribonucleotides (dNTPs), the building blocks for DNA synthesis and repair. Although any living cell must contain one RNR activity to continue living, bacteria have the capacity to encode different RNR classes in the same genome, allowing them to adapt to different environments and growing conditions. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is well known for its adaptability and surprisingly encodes all three known RNR classes (Ia, II and III). There must be a complex transcriptional regulation network behind this RNR activity, dictating which RNR class will be expressed according to specific growing conditions. In this work, we aim to uncover the role of the transcriptional regulator NrdR in P. aeruginosa. We demonstrate that NrdR regulates all three RNR classes, being involved in differential control depending on whether the growth conditions are aerobic or anaerobic. Moreover, we also identify for the first time that NrdR is not only involved in controlling RNR expression but also regulates topoisomerase I (topA) transcription. Finally, to obtain the entire picture of NrdR regulon, we performed a global transcriptomic analysis comparing the transcription profile of wild-type and nrdR mutant strains. The results provide many new data about the regulatory network that controls P. aeruginosa RNR transcription, bringing us a step closer to the understanding of this complex system.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Stover CK, Pham XQ, Erwin AL, Mizoguchi SD, Warrener P, Hickey MJ, et al. (2000) Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01, an opportunistic pathogen. Nature 406: 959–964. - PubMed
-
- Torrents E, Sahlin M, Sjöberg B-M (2008) The Ribonucleotide Reductase Family- Genetics and Genomics In: Ribonucleotide Reductases (ed KK Andersson) Nova Science Publishers: pp. 17–77.
-
- Nordlund P, Reichard P (2006) Ribonucleotide reductases. Annu Rev Biochem 75: 681–706. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

