ADAM12-directed ectodomain shedding of E-cadherin potentiates trophoblast fusion
- PMID: 25909890
- PMCID: PMC4816105
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2015.44
ADAM12-directed ectodomain shedding of E-cadherin potentiates trophoblast fusion
Abstract
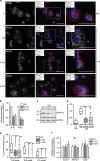
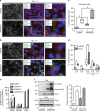
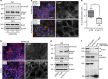
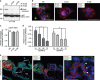
Trophoblasts, placental cells of epithelial lineage, undergo extensive differentiation to form the cellular components of the placenta. Trophoblast progenitor cell differentiation into the multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast is a key developmental process required for placental function, where defects in syncytiotrophoblast formation and turnover associate with placental pathologies and link to poor pregnancy outcomes. The cellular and molecular processes governing syncytiotrophoblast formation are poorly understood, but require the activation of pathways that direct cell fusion. The protease, A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase 12 (ADAM12), controls cell fusion in myoblasts and is highly expressed in the placenta localizing to multiple trophoblast populations. However, the importance of ADAM12 in regulating trophoblast fusion is unknown. Here, we describe a function for ADAM12 in regulating trophoblast fusion. Using two distinct trophoblast models of cell fusion, we show that ADAM12 is dynamically upregulated and is under the transcriptional control of protein kinase A. siRNA-directed loss of ADAM12 impedes spontaneous fusion of primary cytotrophoblasts, whereas overexpression of the secreted variant, ADAM12S, potentiates cell fusion in the Bewo trophoblast cell line. Mechanistically, both ectopic and endogenous levels of ADAM12 were shown to control trophoblast fusion through E-cadherin ectodomain shedding and remodeling of intercellular boundaries. This study describes a novel role for ADAM12 in placental development, specifically highlighting its importance in controlling the differentiation of villous cytotrophoblasts into multinucleated cellular structures. Moreover, this work identifies E-cadherin as a novel ADAM12 substrate, and highlights the significance that cell adhesion molecule ectodomain shedding has in normal development.
Figures
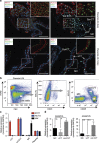
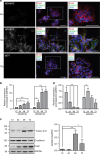
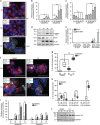
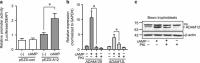
References
-
- Pijnenborg R, Vercruysse L, Carter AM. Deep trophoblast invasion and spiral artery remodelling in the placental bed of the chimpanzee. Placenta 2011; 32: 400–408. - PubMed
-
- Avagliano L, Marconi AM, Romagnoli S, Bulfamante GP. Abnormal spiral arteries modification in stillbirths: the role of maternal prepregnancy body mass index. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2012; 25: 2789–2792. - PubMed
-
- Oren-Suissa M, Podbilewicz B. Cell fusion during development. Trends Cell Biol 2007; 17: 537–546. - PubMed
-
- Chaddha V, Viero S, Huppertz B, Kingdom J. Developmental biology of the placenta and the origins of placental insufficiency. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2004; 9: 357–369. - PubMed
-
- Pidoux G, Gerbaud P, Dompierre J, Lygren B, Solstad T, Evain-Brion D et al. A PKA-ezrin-connexin 43 signaling complex controls gap junction communication and thereby trophoblast cell fusion. J Cell Sci 2014; 127: 4172–4185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

