The Development and Evaluation of a Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Method for the Rapid Detection of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi
- PMID: 25910059
- PMCID: PMC4409374
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124507
The Development and Evaluation of a Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Method for the Rapid Detection of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi
Abstract
Typhoid fever remains a public health threat in many countries. A positive result in traditional culture is a gold-standard for typhoid diagnosis, but this method is time consuming and not sensitive enough for detection of samples containing a low copy number of the target organism. The availability of the loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay, which offers high speed and simplicity in detection of specific targets, has vastly improved the diagnosis of numerous infectious diseases. However, little research efforts have been made on utilizing this approach for diagnosis of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi by targeting a single and specific gene. In this study, a LAMP assay for rapid detection of S. Typhi based on a novel marker gene, termed STY2879-LAMP, was established and evaluated with real-time PCR (RT-PCR). The specificity tests showed that STY2879 could be amplified in all S. Typhi strains isolated in different years and regions in China, whereas no amplification was observable in non-typhoidal strains covering 34 Salmonella serotypes and other pathogens causing febrile illness. The detection limit of STY2879-LAMP for S. Typhi was 15 copies/reaction in reference plasmids, 200 CFU/g with simple heat-treatment of DNA extracted from simulated stool samples and 20 CFU/ml with DNA extracted from simulated blood samples, which was 10 fold more sensitive than the parallel RT-PCR control experiment. Furthermore, the sensitivity of STY2879-LAMP and RT-PCR combining the traditional culture enrichment method for simulated stool and blood spiked with lower S. Typhi count during the 10 h enrichment time was also determined. In comparison with LAMP, the positive reaction time for RT-PCR required additional 2-3 h enrichment time for either simulated stool or blood specimens. Therefore, STY2879-LAMP is of practical value in the clinical settings and has a good potential for application in developing regions due to its easy-to-use protocol.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

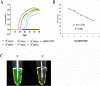
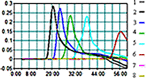

Similar articles
-
Rapid and Sensitive Salmonella Typhi Detection in Blood and Fecal Samples Using Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification.Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2015 Sep;12(9):778-86. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2015.1950. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2015. PMID: 26270463
-
Robustness of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction for diagnostic applications.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2011 Jun;62(1):41-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2011.00785.x. Epub 2011 Mar 16. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21276085
-
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification-based detection of typhoid fever on an automated Genie II Mk2 system - A case-control-based approach.Acta Trop. 2019 Feb;190:293-295. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.12.004. Epub 2018 Dec 5. Acta Trop. 2019. PMID: 30528158
-
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): A novel rapid detection platform for pathogens.Microb Pathog. 2017 Jun;107:54-61. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.03.016. Epub 2017 Mar 18. Microb Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28323152 Review.
-
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi and gallbladder cancer: a case-control study and meta-analysis.Cancer Med. 2016 Nov;5(11):3310-3235. doi: 10.1002/cam4.915. Epub 2016 Oct 11. Cancer Med. 2016. PMID: 27726295 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasensitive cloth-based microfluidic chemiluminescence detection of Listeria monocytogenes hlyA gene by hemin/G-quadruplex DNAzyme and hybridization chain reaction signal amplification.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020 Jun;412(15):3787-3797. doi: 10.1007/s00216-020-02633-5. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020. PMID: 32306067
-
Rapid detection of Clostridium perfringens in food by loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with a lateral flow biosensor.PLoS One. 2021 Jan 7;16(1):e0245144. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245144. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33411848 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Typhoidal and Paratyphoidal Salmonella in Blood by Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction.Clin Infect Dis. 2015 Nov 1;61 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S241-50. doi: 10.1093/cid/civ726. Clin Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26449938 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Detection Device for Salmonella typhi in Milk, Juice, Water and Calf Serum.Indian J Microbiol. 2018 Sep;58(3):381-392. doi: 10.1007/s12088-018-0730-4. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Indian J Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30013283 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the stability of lyophilized loop-mediated isothermal amplification reagents for the detection of Coxiella burnetii.Heliyon. 2017 Oct 6;3(10):e00415. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2017.e00415. eCollection 2017 Oct. Heliyon. 2017. PMID: 29057336 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Petit PL, Wamola IA. Typhoid fever: a review of its impact and diagnostic problems. East African medical journal. 1994;71(3):183–188. - PubMed
-
- Murdoch DR, Woods CW, Zimmerman MD, Dull PM, Belbase RH, Keenan AJ, et al. The etiology of febrile illness in adults presenting to Patan hospital in Kathmandu, Nepal. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004;70(6):670–675. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Background document: The diagnosis, treatment and prevention of typhoid fever. Communicable Disease Surveillance and Response Vaccines and Biologicals. 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

