Novel cancer chemotherapy hits by molecular topology: dual Akt and Beta-catenin inhibitors
- PMID: 25910265
- PMCID: PMC4409212
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124244
Novel cancer chemotherapy hits by molecular topology: dual Akt and Beta-catenin inhibitors
Abstract
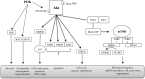
Background and purpose: Colorectal and prostate cancers are two of the most common types and cause of a high rate of deaths worldwide. Therefore, any strategy to stop or at least slacken the development and progression of malignant cells is an important therapeutic choice. The aim of the present work is the identification of novel cancer chemotherapy agents. Nowadays, many different drug discovery approaches are available, but this paper focuses on Molecular Topology, which has already demonstrated its extraordinary efficacy in this field, particularly in the identification of new hit and lead compounds against cancer. This methodology uses the graph theoretical formalism to numerically characterize molecular structures through the so called topological indices. Once obtained a specific framework, it allows the construction of complex mathematical models that can be used to predict physical, chemical or biological properties of compounds. In addition, Molecular Topology is highly efficient in selecting and designing new hit and lead drugs. According to the aforementioned, Molecular Topology has been applied here for the construction of specific Akt/mTOR and β-catenin inhibition mathematical models in order to identify and select novel antitumor agents.
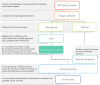
Experimental approach: Based on the results obtained by the selected mathematical models, six novel potential inhibitors of the Akt/mTOR and β-catenin pathways were identified. These compounds were then tested in vitro to confirm their biological activity.
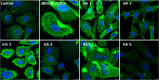
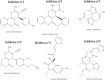
Conclusion and implications: Five of the selected compounds, CAS n° 256378-54-8 (Inhibitor n°1), 663203-38-1 (Inhibitor n°2), 247079-73-8 (Inhibitor n°3), 689769-86-6 (Inhibitor n°4) and 431925-096 (Inhibitor n°6) gave positive responses and resulted to be active for Akt/mTOR and/or β-catenin inhibition. This study confirms once again the Molecular Topology's reliability and efficacy to find out novel drugs in the field of cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discovery and SAR exploration of a novel series of imidazo[4,5-b]pyrazin-2-ones as potent and selective mTOR kinase inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011 Nov 15;21(22):6793-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.09.035. Epub 2011 Sep 16. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011. PMID: 21978683
-
Discovery of 1-(3-aryl-4-chlorophenyl)-3-(p-aryl)urea derivatives against breast cancer by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Hedgehog signalings.Eur J Med Chem. 2017 Dec 1;141:721-733. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.09.002. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Eur J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 29107429
-
Isobavachalcone isolated from Psoralea corylifolia inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis via inhibiting the AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway in colorectal cancer cells.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 May 1;13:1449-1460. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S192681. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31118579 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway inhibitors in cancer: a perspective on clinical progress.Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(35):4326-41. doi: 10.2174/092986710793361234. Curr Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20939811 Review.
-
Protein kinases as targets for developing anticancer agents from marine organisms.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2021 Jan;1865(1):129759. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2020.129759. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2021. PMID: 33038451 Review.
Cited by
-
Similarity-Based Virtual Screening to Find Antituberculosis Agents Based on Novel Scaffolds: Design, Syntheses and Pharmacological Assays.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 1;23(23):15057. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315057. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499384 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular topology and QSAR multi-target analysis to boost the in silico research for fungicides in agricultural chemistry.Mol Divers. 2019 May;23(2):371-379. doi: 10.1007/s11030-018-9879-3. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Mol Divers. 2019. PMID: 30284694
-
In Silico Approaches In Carcinogenicity Hazard Assessment: Current Status and Future Needs.Comput Toxicol. 2021 Nov;20:100191. doi: 10.1016/j.comtox.2021.100191. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Comput Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 35368437 Free PMC article.
-
Rational Design of Chitin Deacetylase Inhibitors for Sustainable Agricultural Use Based on Molecular Topology.J Agric Food Chem. 2022 Oct 19;70(41):13118-13131. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c02377. Epub 2022 Oct 4. J Agric Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 36194443 Free PMC article.
-
New Pharmacokinetic and Microbiological Prediction Equations to Be Used as Models for the Search of Antibacterial Drugs.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jan 20;15(2):122. doi: 10.3390/ph15020122. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35215235 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

