A Multicenter, Phase II, Randomized, Noncomparative Clinical Trial of Radiation and Temozolomide with or without Vandetanib in Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma Patients
- PMID: 25910950
- PMCID: PMC4790106
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-3220
A Multicenter, Phase II, Randomized, Noncomparative Clinical Trial of Radiation and Temozolomide with or without Vandetanib in Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma Patients
Abstract
Purpose: Vandetanib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor of KDR (VEGFR2), EGFR, and RET, may enhance sensitivity to chemotherapy and radiation. We conducted a randomized, noncomparative, phase II study of radiation (RT) and temozolomide with or without vandetanib in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma (GBM).
Experimental design: We planned to randomize a total of 114 newly diagnosed GBM patients in a ratio of 2:1 to standard RT and temozolomide with (76 patients) or without (38 patients) vandetanib 100 mg daily. Patients with age ≥ 18 years, Karnofsky performance status (KPS) ≥ 60, and not on enzyme-inducing antiepileptics were eligible. Primary endpoint was median overall survival (OS) from the date of randomization. Secondary endpoints included median progression-free survival (PFS), 12-month PFS, and safety. Correlative studies included pharmacokinetics as well as tissue and serum biomarker analysis.
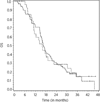
Results: The study was terminated early for futility based on the results of an interim analysis. We enrolled 106 patients (36 in the RT/temozolomide arm and 70 in the vandetanib/RT/temozolomide arm). Median OS was 15.9 months [95% confidence interval (CI), 11.0-22.5 months] in the RT/temozolomide arm and 16.6 months (95% CI, 14.9-20.1 months) in the vandetanib/RT/temozolomide (log-rank P = 0.75).
Conclusions: The addition of vandetanib at a dose of 100 mg daily to standard chemoradiation in patients with newly diagnosed GBM or gliosarcoma was associated with potential pharmacodynamic biomarker changes and was reasonably well tolerated. However, the regimen did not significantly prolong OS compared with the parallel control arm, leading to early termination of the study.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
A.B. Lassman is a consultant/advisory board member for Agenus, Amgen, Celgene, Foundation Medicine, Genentech, Heron, Kyowa Hakko Kirin Pharma, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Midatech, Novartis, Roche, Sigma Tau, and Stemline. R. Beroukhim has ownership interest (including patents) in Astra-Zeneca. T. Batchelor reports receiving commercial research grants from Astra-Zeneca, Millennium, and Pfizer; speakers bureau honoraria from Champions Biotechnology, Educational Concepts Group, Imedex, Oakstone Publishing, Research to Practice, Robert Michael Educational Institute, and Up to Date, Inc; and is a consultant/advisory board member for Agenus, Amgen, Kirin, Merck, Novartis, Proximagen, Roche, and Spectrum. P.Y. Wen reports receiving other research grants from AbbVie, Agios, Angiochem, Ascular Biogenics, AstraZeneca, Cubist, Exelixis, Genentech/Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, Karyopharm, Merck, Novartis, and Sanofi-Aventis; speakers bureau honoraria from Merck; and is a consultant/advisory board member for AbbVie, Celldex, Genentech/Roche, Midatech, Momenta, Novartis, Novocure, Sigma Tau, and Vascular Biogenics. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
Figures
References
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–996. - PubMed
-
- Nicholas MK, Lukas RV, Jafri NF, Faoro L, Salgia R. Epidermal growth factor receptor - mediated signal transduction in the development and therapy of gliomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:7261–7270. - PubMed
-
- Li B, Yuan M, Kim IA, Chang CM, Bernhard EJ, Shu HK. Mutant epidermal growth factor receptor displays increased signaling through the phospha-tidylinositol-3 kinase/AKT pathway and promotes radioresistance in cells of astrocytic origin. Oncogene. 2004;23:4594–4602. - PubMed
-
- Chakravarti A, Chakladar A, Delaney MA, Latham DE, Loeffler JS. The epidermal growth factor receptor pathway mediates resistance to sequential administration of radiation and chemotherapy in primary human glioblastoma cells in a RAS-dependent manner. Cancer Res. 2002;62:4307–4315. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous