Structural and Biochemical Basis for the Inhibitory Effect of Liprin-α3 on Mouse Diaphanous 1 (mDia1) Function
- PMID: 25911102
- PMCID: PMC4505501
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.621946
Structural and Biochemical Basis for the Inhibitory Effect of Liprin-α3 on Mouse Diaphanous 1 (mDia1) Function
Abstract
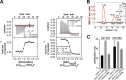
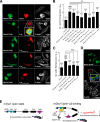
Diaphanous-related formins are eukaryotic actin nucleation factors regulated by an autoinhibitory interaction between the N-terminal RhoGTPase-binding domain (mDiaN) and the C-terminal Diaphanous-autoregulatory domain (DAD). Although the activation of formins by Rho proteins is well characterized, its inactivation is only marginally understood. Recently, liprin-α3 was shown to interact with mDia1. Overexpression of liprin-α3 resulted in a reduction of the cellular actin filament content. The molecular mechanisms of how liprin-α3 exerts this effect and counteracts mDia1 activation by RhoA are unknown. Here, we functionally and structurally define a minimal liprin-α3 core region, sufficient to recapitulate the liprin-α3 determined mDia1-respective cellular functions. We show that liprin-α3 alters the interaction kinetics and thermodynamics of mDiaN with RhoA·GTP and DAD. RhoA displaces liprin-α3 allosterically, whereas DAD competes with liprin-α3 for a highly overlapping binding site on mDiaN. Liprin-α3 regulates actin polymerization by lowering the regulatory potency of RhoA and DAD on mDiaN. We present a model of a mechanistically unexplored and new aspect of mDiaN regulation by liprin-α3.
Keywords: Ras homolog gene family, member A (RhoA); actin; cytoskeleton; formin; liprin; mDia1.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Biochemical characterization of the Rho GTPase-regulated actin assembly by diaphanous-related formins, mDia1 and Daam1, in platelets.J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 28;283(13):8746-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707839200. Epub 2008 Jan 24. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18218625
-
Dissecting requirements for auto-inhibition of actin nucleation by the formin, mDia1.J Biol Chem. 2005 Feb 25;280(8):6986-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M411605200. Epub 2004 Dec 9. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15591319
-
Structure and activity of full-length formin mDia1.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2012 Jun;69(6):393-405. doi: 10.1002/cm.21033. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2012. PMID: 22605659 Free PMC article.
-
Formin proteins: a domain-based approach.Trends Biochem Sci. 2005 Jun;30(6):342-53. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2005.04.014. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005. PMID: 15950879 Review.
-
FHOD proteins in actin dynamics--a formin' class of its own.Small GTPases. 2014;5(2):11. doi: 10.4161/21541248.2014.973765. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 25483300 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural insights into selective interaction between type IIa receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases and Liprin-α.Nat Commun. 2020 Jan 31;11(1):649. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14516-5. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32005855 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear protein FNBP4: A novel inhibitor of non-diaphanous formin FMN1-mediated actin cytoskeleton dynamics.J Biol Chem. 2025 Jun;301(6):108550. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108550. Epub 2025 Apr 30. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40316024 Free PMC article.
-
Liprins in oncogenic signaling and cancer cell adhesion.Oncogene. 2021 Nov;40(46):6406-6416. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-02048-1. Epub 2021 Oct 15. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 34654889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The scaffold-protein IQGAP1 enhances and spatially restricts the actin-nucleating activity of Diaphanous-related formin 1 (DIAPH1).J Biol Chem. 2020 Mar 6;295(10):3134-3147. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010476. Epub 2020 Jan 31. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32005666 Free PMC article.
-
Liprin-α-Mediated Assemblies and Their Roles in Synapse Formation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 19;9:653381. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.653381. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33869211 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li F., Higgs H. N. (2005) Dissecting requirements for auto-inhibition of actin nucleation by the formin, mDia1. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 6986–6992 - PubMed
-
- Machaidze G., Sokoll A., Shimada A., Lustig A., Mazur A., Wittinghofer A., Aebi U., Mannherz H. G. (2010) Actin filament bundling and different nucleating effects of mouse Diaphanous-related formin FH2 domains on actin/ADF and actin/cofilin complexes. J. Mol. Biol. 403, 529–545 - PubMed
-
- Zigmond S. H. (2004) Formin-induced nucleation of actin filaments. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 16, 99–105 - PubMed
-
- Pring M., Evangelista M., Boone C., Yang C., Zigmond S. H. (2003) Mechanism of formin-induced nucleation of actin filaments. Biochemistry 42, 486–496 - PubMed
-
- Kovar D. R., Pollard T. D. (2004) Progressing actin: formin as a processive elongation machine. Nat. Cell Biol. 6, 1158–1159 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

