Functionally different PIN proteins control auxin flux during bulbil development in Agave tequilana
- PMID: 25911746
- PMCID: PMC4473989
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erv191
Functionally different PIN proteins control auxin flux during bulbil development in Agave tequilana
Abstract
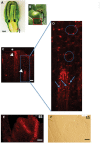
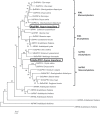
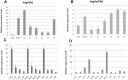
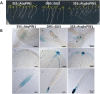
In Agave tequilana, reproductive failure or inadequate flower development stimulates the formation of vegetative bulbils at the bracteoles, ensuring survival in a hostile environment. Little is known about the signals that trigger this probably unique phenomenon in agave species. Here we report that auxin plays a central role in bulbil development and show that the localization of PIN1-related proteins is consistent with altered auxin transport during this process. Analysis of agave transcriptome data led to the identification of the A. tequilana orthologue of PIN1 (denoted AtqPIN1) and a second closely related gene from a distinct clade reported as 'Sister of PIN1' (denoted AtqSoPIN1). Quantitative real-time reverse transcription-PCR (RT-qPCR) analysis showed different patterns of expression for each gene during bulbil formation, and heterologous expression of the A. tequilana PIN1 and SoPIN1 genes in Arabidopsis thaliana confirmed functional differences between these genes. Although no free auxin was detected in induced pedicel samples, changes in the levels of auxin precursors were observed. Taken as a whole, the data support the model that AtqPIN1 and AtqSoPIN1 have co-ordinated but distinct functions in relation to auxin transport during the initial stages of bulbil formation.
Keywords: Agave tequilana; PIN proteins.; auxin flux; bulbil; development; gene expression; immunolocalization.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Experimental Biology.
Figures



References
-
- Abraham-Juarez MJ, Martinez-Hernandez A, Leyva-Gonzalez MA, Herrera-Estrella L, Simpson J. 2010. Class I KNOX genes are associated with organogenesis during bulbil formation in Agave tequilana. Journal of Experimental Botany 61, 4055–4067. - PubMed
-
- Arizaga S, Ezcurra E. 1995. Insurance against reproductive failure in a semelparous plant—bulbil formation in Agave macroacantha flowering stalks. Oecologia 101, 329–334. - PubMed
-
- Arizaga S, Ezcurra E. 2002. Propagation mechanisms in Agave macroacantha (Agavaceae), a tropical arid-land succulent rosette. American Journal of Botany 89, 632–641. - PubMed
-
- Arizaga S, Ezcurra E, Peters E, de Arellano FR, Vega E. 2000. a . Pollination ecology of Agave macroacantha (Agavaceae) in a Mexican tropical desert. I. Floral biology and pollination mechanisms. American Journal of Botany 87, 1004–1010. - PubMed
-
- Arizaga S, Ezcurra E, Peters E, de Arellano FR, Vega E. 2000. b Pollination ecology of Agave macroacantha (Agavaceae) in a Mexican tropical desert. II. The role of pollinators. American Journal of Botany 87, 1011–1017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

