Importance of imaging and recent developments in diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 25914777
- PMCID: PMC4404382
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i5.769
Importance of imaging and recent developments in diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is one of the most common causes of chronic liver disease and is a major public health problem worldwide. It is a spectrum that includes simple steatosis, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis and cirrhosis. Recently, NAFLD prevalence in children and adolescents has increased too. The increasing prevalence has resulted in NASH-related chronic liver disease. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment is quite important. Although liver biopsy is still the gold standard for diagnosis and staging of NAFLD, particularly for the diagnosis of NASH, imaging methods such as ultrasonography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging with chemical shift imaging and especially magnetic resonance spectroscopy and elastography have been increasingly approved as noninvasive alternative methods. The aim of this review is to analyze the diagnostic accuracy and limitations of the imaging methods and recent developments in the diagnosis of NAFLD.
Keywords: Elastography; Imaging methods; Magnetic resonance spectroscopy; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Figures
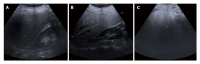
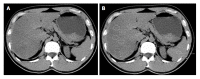
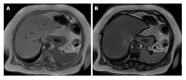
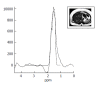
References
-
- Sanyal AJ. NASH: A global health problem. Hepatol Res. 2011;41:670–674. - PubMed
-
- Polyzos SA, Kountouras J, Zavos C, Deretzi G. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: multimodal treatment options for a pathogenetically multiple-hit disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2012;46:272–284. - PubMed
-
- Koplay M, Gulcan E, Ozkan F. Association between serum vitamin B12 levels and the degree of steatosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Investig Med. 2011;59:1137–1140. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

