Human definitive haemogenic endothelium and arterial vascular endothelium represent distinct lineages
- PMID: 25915127
- PMCID: PMC4551438
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb3161
Human definitive haemogenic endothelium and arterial vascular endothelium represent distinct lineages
Abstract
The generation of haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) from human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) will depend on the accurate recapitulation of embryonic haematopoiesis. In the early embryo, HSCs develop from the haemogenic endothelium (HE) and are specified in a Notch-dependent manner through a process named endothelial-to-haematopoietic transition (EHT). As HE is associated with arteries, it is assumed that it represents a subpopulation of arterial vascular endothelium (VE). Here we demonstrate at a clonal level that hPSC-derived HE and VE represent separate lineages. HE is restricted to the CD34(+)CD73(-)CD184(-) fraction of day 8 embryoid bodies and it undergoes a NOTCH-dependent EHT to generate RUNX1C(+) cells with multilineage potential. Arterial and venous VE progenitors, in contrast, segregate to the CD34(+)CD73(med)CD184(+) and CD34(+)CD73(hi)CD184(-) fractions, respectively. Together, these findings identify HE as distinct from VE and provide a platform for defining the signalling pathways that regulate their specification to functional HSCs.
Figures
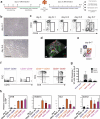
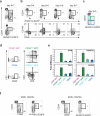

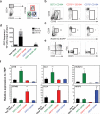
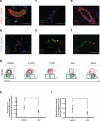

References
-
- Kennedy M, et al. T lymphocyte potential marks the emergence of definitive hematopoietic progenitors in human pluripotent stem cell differentiation cultures. Cell reports. 2012;2:1722–1735. - PubMed
-
- Klimchenko O, et al. Monocytic cells derived from human embryonic stem cells and fetal liver share common differentiation pathways and homeostatic functions. Blood. 2011;117:3065–3075. - PubMed
-
- Takayama N, et al. Generation of functional platelets from human embryonic stem cells in vitro via ES-sacs, VEGF-promoted structures that concentrate hematopoietic progenitors. Blood. 2008;111:5298–5306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

