Improved genome inference in the MHC using a population reference graph
- PMID: 25915597
- PMCID: PMC4449272
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3257
Improved genome inference in the MHC using a population reference graph
Abstract
Although much is known about human genetic variation, such information is typically ignored in assembling new genomes. Instead, reads are mapped to a single reference, which can lead to poor characterization of regions of high sequence or structural diversity. We introduce a population reference graph, which combines multiple reference sequences and catalogs of variation. The genomes of new samples are reconstructed as paths through the graph using an efficient hidden Markov model, allowing for recombination between different haplotypes and additional variants. By applying the method to the 4.5-Mb extended MHC region on human chromosome 6, combining 8 assembled haplotypes, the sequences of known classical HLA alleles and 87,640 SNP variants from the 1000 Genomes Project, we demonstrate using simulations, SNP genotyping, and short-read and long-read data how the method improves the accuracy of genome inference and identified regions where the current set of reference sequences is substantially incomplete.
Figures
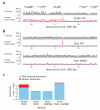

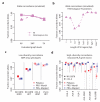
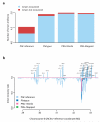

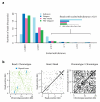
References
-
- Zook JM, et al. Integrating human sequence data sets provides a resource of benchmark SNP and indel genotype calls. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32:246–251. - PubMed
Methods only references
-
- Holdsworth R, et al. The HLA dictionary 2008: a summary of HLA-A, -B, -C, -DRB1/3/4/5, and -DQB1 alleles and their association with serologically defined HLA-A, -B, -C, -DR, and -DQ antigens. Tissue Antigens. 2009;73:95–170. - PubMed
-
- Spraggs CF, Parham LR, Hunt CM, Dollery CT. Lapatinib-induced liver injury characterized by class II HLA and Gilbert’s syndrome genotypes. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012;91:647–652. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

