Computational Tools for Interpreting Ion Channel pH-Dependence
- PMID: 25915903
- PMCID: PMC4411139
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125293
Computational Tools for Interpreting Ion Channel pH-Dependence
Abstract
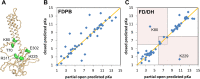
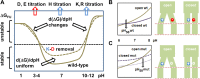
Activity in many biological systems is mediated by pH, involving proton titratable groups with pKas in the relevant pH range. Experimental analysis of pH-dependence in proteins focusses on particular sidechains, often with mutagenesis of histidine, due to its pKa near to neutral pH. The key question for algorithms that predict pKas is whether they are sufficiently accurate to effectively narrow the search for molecular determinants of pH-dependence. Through analysis of inwardly rectifying potassium (Kir) channels and acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs), mutational effects on pH-dependence are probed, distinguishing between groups described as pH-coupled or pH-sensor. Whereas mutation can lead to a shift in transition pH between open and closed forms for either type of group, only for pH-sensor groups does mutation modulate the amplitude of the transition. It is shown that a hybrid Finite Difference Poisson-Boltzmann (FDPB) - Debye-Hückel continuum electrostatic model can filter mutation candidates, providing enrichment for key pH-coupled and pH-sensor residues in both ASICs and Kir channels, in comparison with application of FDPB alone.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Srivastava J, Barber DL, Jacobson MP (2007) Intracellular pH sensors: design principles and functional significance. Physiology (Bethesda) 22: 30–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

