Latent structure of cognition in schizophrenia: a confirmatory factor analysis of the MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery (MCCB)
- PMID: 25916421
- PMCID: PMC4523424
- DOI: 10.1017/S0033291715000641
Latent structure of cognition in schizophrenia: a confirmatory factor analysis of the MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery (MCCB)
Erratum in
-
Latent structure of cognition in schizophrenia: a confirmatory factor analysis of the MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery (MCCB).Psychol Med. 2016 Apr;46(5):1119. doi: 10.1017/S0033291715002433. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Psychol Med. 2016. PMID: 26537981 No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The number of separable cognitive dimensions in schizophrenia has been debated. Guided by the extant factor analytic literature, the NIMH Measurement and Treatment Research to Improve Cognition in Schizophrenia (MATRICS) initiative selected seven cognitive domains relevant to treatment studies in schizophrenia: speed of processing, attention/vigilance, working memory, verbal learning, visual learning, reasoning and problem solving, and social cognition. These domains are assessed in the MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery (MCCB). The aim of this study was to conduct a confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) of the beta battery of the MCCB to compare the fit of the MATRICS consensus seven-domain model to other models in the current literature on cognition in schizophrenia.
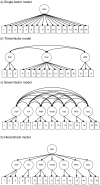
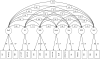
Method: Using data from 281 schizophrenia outpatients, we compared the seven correlated factors model with alternative models. Specifically, we compared the 7-factor model to (a) a single-factor model, (b) a three correlated factors model including speed of processing, working memory, and general cognition, and (c) a hierarchical model in which seven first-order factors loaded onto a second-order general cognitive factor.
Results: Multiple fit indices indicated the seven correlated factors model was the best fit for the data and provided significant improvement in model fit beyond the comparison models.
Conclusions: These results support the assessment of these seven cognitive dimensions in clinical trials of interventions to improve cognition in schizophrenia. Because these cognitive factors are separable to some degree, it is plausible that specific interventions may have differential effects on the domains.
Keywords: Confirmatory factor analysis; MCCB; neurocognition; schizophrenia.
Figures
References
-
- Allen DN, Strauss GP, Donohue B, van Kammen DP. Factor analytic support for social cognition as a separable cognitive domain in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research. 2007;93:325–33. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV) American Psychiatric Press; Washington, DC: 1994.
-
- Army US. Army Individual Test Battery: Manual of Directions and Scoring. Adjutant General's Office, War Department; Washington, D C: 1944.
-
- Arnau RC, Thompson B. Second-order confirmatory factor analysis of the WAIS-III. Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale. Assessment. 2000;7:237–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

