A dichoptic custom-made action video game as a treatment for adult amblyopia
- PMID: 25917239
- PMCID: PMC4549206
- DOI: 10.1016/j.visres.2015.04.008
A dichoptic custom-made action video game as a treatment for adult amblyopia
Abstract
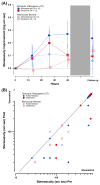
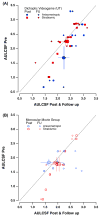
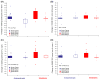
Previous studies have employed different experimental approaches to enhance visual function in adults with amblyopia including perceptual learning, videogame play, and dichoptic training. Here, we evaluated the efficacy of a novel dichoptic action videogame combining all three approaches. This experimental intervention was compared to a conventional, yet unstudied method of supervised occlusion while watching movies. Adults with unilateral amblyopia were assigned to either play the dichoptic action game (n=23; 'game' group), or to watch movies monocularly while the fellow eye was patched (n=15; 'movies' group) for a total of 40hours. Following training, visual acuity (VA) improved on average by ≈0.14logMAR (≈28%) in the game group, with improvements noted in both anisometropic and strabismic patients. This improvement is similar to that obtained following perceptual learning, video game play or dichoptic training. Surprisingly, patients with anisometropic amblyopia in the movies group showed similar improvement, revealing a greater impact of supervised occlusion in adults than typically thought. Stereoacuity, reading speed, and contrast sensitivity improved more for game group participants compared with movies group participants. Most improvements were largely retained following a 2-month no-contact period. This novel video game, which combines action gaming, perceptual learning and dichoptic presentation, results in VA improvements equivalent to those previously documented with each of these techniques alone. Our game intervention led to greater improvement than control training in a variety of visual functions, thus suggesting that this approach has promise for the treatment of adult amblyopia.
Keywords: Amblyopia; Perceptual learning; Stereopsis; Suppression; Videogames; Visual acuity.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors DB and DL have filed a patent for a dichoptic treatment method, however none of the authors have a commercial conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Baker DH, Meese TS, Hess RF. Contrast masking in strabismic amblyopia: Attenuation, noise, interocular suppression and binocular summation. Vision Research. 2008;48:1625–1640. - PubMed
-
- Bavelier D, Green CS, Pouget A, Schrater P. Brain plasticity through the life span: Learning to learn and action video games. Annual Review of Neuroscience. 2012;35:391–416. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

