Imidazole-based alkaloid derivative LCB54-0009 suppresses ocular angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in models of experimental retinopathy and corneal neovascularization
- PMID: 25917462
- PMCID: PMC4523342
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13177
Imidazole-based alkaloid derivative LCB54-0009 suppresses ocular angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in models of experimental retinopathy and corneal neovascularization
Abstract
Background and purpose: Abnormally induced angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis are associated with human diseases, including neovascular eye disease. Substances that inhibit these processes may have potential as an attractive therapeutic strategy for these diseases.
Experimental approach: In vitro and in vivo angiogenesis and/or lymphangiogenesis were assessed in VEGF- or hypoxia-stimulated endothelial and retinal cells and in animal models of oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR), streptozotocin-induced diabetic retinopathy (SIDR), suture-induced inflammatory corneal neovascularization (SICNV) and silver nitrate-induced corneal neovascularization. HUVECs and retinal cells were cultured under hypoxic conditions or incubated with VEGF to identify the molecular mechanisms involved.
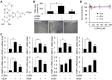
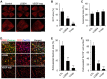
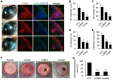
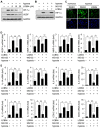
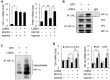
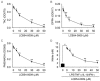
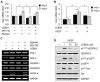
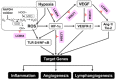
Key results: The imidazole-based alkaloid derivative LCB54-0009 inhibited capillary-like tube formation in VEGF-induced HUVECs without inducing cytotoxic effects. Intravitreal injection of LCB54-0009 into retinas suppressed the formation of the pathological neovascular tufts and increased vascular permeability in both OIR of mice and SIDR of rats. Furthermore, subconjunctival injection of LCB54-0009 into the cornea suppressed corneal inflammation and inflammation-associated angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in SICNV of mice and silver nitrate cauterization of rats. These pharmacological activities were associated with effects on HIF-1α protein stability and HIF-1α/NF-κB redox sensitivity through its antioxidant activities. LCB54-0009 also inhibited the hypoxia-induced expression of angiopoietin-2, and VEGF-induced VEGFR-2 activation and downstream signalling, resulting in the down-regulation of the expression of pro-angiogenic factors and pro-inflammatory mediators and an up-regulation of the expression of anti-angiogenic factors.
Conclusions and implications: LCB54-0009 is a potential candidate molecule for blocking pathological angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis mediated by HIF-1α- angiopoietin-2 expression and VEGFR-2 activation.
© 2015 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sunitinib inhibits inflammatory corneal lymphangiogenesis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 May 3;54(5):3082-93. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-10856. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23580490
-
Celecoxib attenuates retinal angiogenesis in a mouse model of oxygen-induced retinopathy.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 May 1;8(5):4990-8. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26191192 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-angiogenic effects of the DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin via inhibition of VEGFR signalling in the mouse model of oxygen-induced retinopathy.Diabetologia. 2018 Nov;61(11):2412-2421. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4701-4. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 30097694
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α: A promising therapeutic target for vasculopathy in diabetic retinopathy.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Sep;159:104924. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104924. Epub 2020 May 25. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32464323 Review.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor system: physiological functions in angiogenesis and pathological roles in various diseases.J Biochem. 2013 Jan;153(1):13-9. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvs136. Epub 2012 Nov 21. J Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23172303 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological Potential of Small Molecules for Treating Corneal Neovascularization.Molecules. 2020 Jul 30;25(15):3468. doi: 10.3390/molecules25153468. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32751576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lymphatic vessel: origin, heterogeneity, biological functions, and therapeutic targets.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Jan 3;9(1):9. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01723-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38172098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current and emerging therapies for corneal neovascularization.Ocul Surf. 2018 Oct;16(4):398-414. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2018.06.004. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Ocul Surf. 2018. PMID: 29908870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Critical Analysis of the Available In Vitro and Ex Vivo Methods to Study Retinal Angiogenesis.J Ophthalmol. 2017;2017:3034953. doi: 10.1155/2017/3034953. Epub 2017 Aug 7. J Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28848677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective effect of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 against rat corneal dysfunction caused by streptozotocin-induced type I diabetes.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021 Aug;246(15):1740-1749. doi: 10.1177/15353702211013308. Epub 2021 May 8. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021. PMID: 33969723 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams RH, Alitalo K. Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:464–478. - PubMed
-
- Arjamaa O, Nikinmaa M. Oxygen-dependent diseases in the retina: role of hypoxia-inducible factors. Exp Eye Res. 2006;83:473–483. - PubMed
-
- Blouin CC, Pagé EL, Soucy GM, Richard DE. Hypoxic gene activation by lipopolysaccharide in macrophages: implication of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Blood. 2004;103:1124–1130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

